For a person whose company is firmly tethered to terra firma, Brad Hartwig spent a long time trying to leave it.
As a high schooler, Hartwig built a pedal-driven helicopter after reading about a human-powered helicopter competition in Popular Science. (It didn’t win.) He then went to USC for aerospace engineering, where he and his team built a rocket to go to space. (It did.) After graduating, Hartwig worked on the engines for SpaceX’s Dragon so the crew and cargo spacecraft could dock with the International Space Station. (It did, safely.)
Then he decided that he didn’t just want to build things that went to space; he wanted to go himself. So he set out to burnish his résumé to become a NASA astronaut candidate, serving in the California Air National Guard and volunteering for Marin County’s search and rescue team responding to wildfires. He also worked for a short time as a flight test engineer for Kittyhawk, the Larry Page–backed, ill-fated e-VTOL startup.
“I held on to the astronaut dream a lot longer than the average kid,” Hartwig told TechCrunch+.
He hasn’t let go entirely, but early last year his life took a bit of a detour when he founded Arbor, a startup that builds specialized power plants to remove carbon dioxide from the air.
It’s cliché to say that everything Hartwig had done in life led him to that point, but in this case, it’s kind of true.
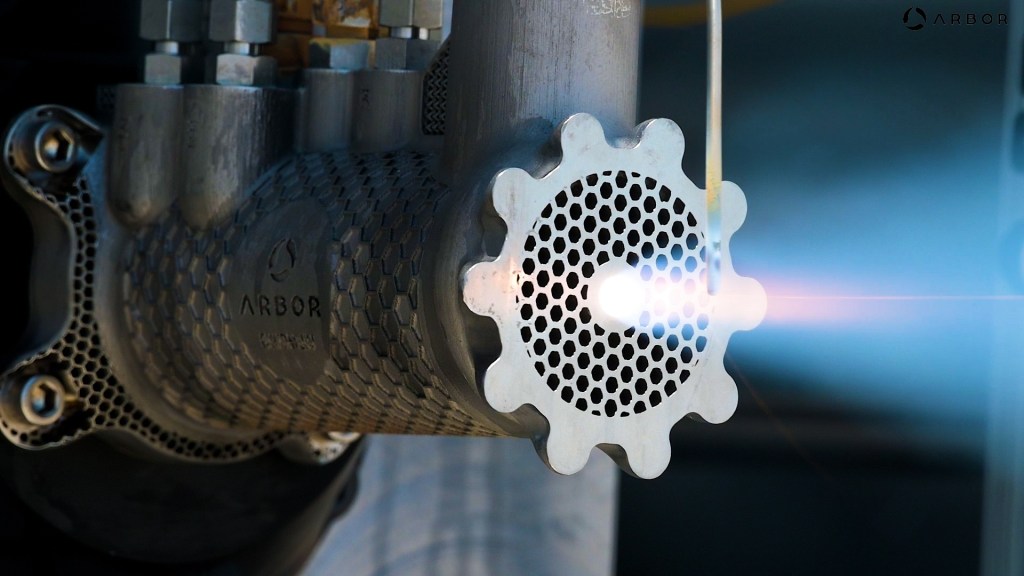
Arbor’s equipment converts waste biomass into syngas, which is then combusted in the presence of pure oxygen to produce pure CO2. The compressed gas is fed through compact turbo machinery similar to that used in SpaceX’s rockets to produce electricity. Hartwig calls it a “vegetarian rocket engine.”
When he first started searching for a way into climate tech, he wasn’t sure his experience at SpaceX would matter, but it turned out to be more applicable than he imagined. Much of Arbor’s technology is derived from the rocket world, including the turbo machinery that generates power and the cryogenic oxygen distillers that supply the oxycombustion unit. His time on the search and rescue team wasn’t wasted, either: He witnessed the massive amount of biomass that resulted from forest-thinning practices meant to reduce wildfire risk. That biomass could become fuel for Arbor’s power plants.
Initially, Hartwig wasn’t planning to become a founder. A few years ago, he considered joining Heirloom, a carbon-removal startup. But his busy training schedule with the California Air National Guard wouldn’t allow it.
He continued studying negative emissions technologies, though, and soon he became enamored with one known as biomass carbon removal and storage, also called BiCRS. BiCRS (pronounced “bikers”) isn’t a new idea, per se, but an evolution of an earlier concept known as bioenergy with carbon capture and sequestration, or BECCS. Essentially, BECCS takes an existing power plant, fuels it with biomass instead of coal or natural gas, and captures the carbon dioxide.
BECCS was a promising technology, but energy experts felt that it had some flaws. Namely, environmentalists were worried that sourcing the biomass would end up doing more harm than good.
BiCRS seeks to solve that problem by essentially turning BECCS on its head. With BiCRS, carbon removal is the primary objective, not a side benefit as it was with BECCS. BiCRS also has no requirement to produce power, as there is with BECCS, though it’s not off the table either. The only real requirements are that biomass does the carbon removal, that the CO2 gets stored for a long time, and that food security, rural livelihoods, and biodiversity are left intact. Ideally, those latter three might actually see some benefits. (Previous bioenergy schemes, like corn ethanol, may have benefited some rural community members but arguably took arable land away from food production.)
Compared with other carbon-removal technologies like direct air capture, which use energy-intensive fans and sorbents to remove CO2 from the air, BiCRS is generally less energy intensive. “It’s thermodynamically the most efficient way of pulling CO2 from the atmosphere because you’re letting plants do the hard work of scrubbing CO2 from the atmosphere,” Hartwig said.
Whether BiCRS is more efficient than direct air capture largely depends on how far biomass needs to be transported. That’s part of the reason why Arbor is designing its power plants to be compact: so they can be sited close to the source.
Part of that compactness comes from the team’s experience designing rockets for SpaceX and turbines for companies like GE. The gas that enters the turbo machinery is highly pressurized, around 150–200 atmospheres (2,200–2,900 psi).
“A biomass boiler for a traditional plant operates around one atmosphere. So we’re thinking about shrinking that hardware by 100x or more,” Hartwig said. “That allows you to have hardware that’s extremely power dense. The turbine is something that fits in your hands.”
Since its founding in 2022, Arbor has been operating quietly, building small demonstrators and working with the Placer County Water Agency in the foothills of California’s Sierra Nevada mountains to construct a pilot plant. The company is also looking into whether its turbo machinery technology can be adapted to retrofit an existing bioenergy plant.
Ultimately, Arbor is hoping to be able to remove a metric ton of carbon for $50 to $100, which is much lower than today’s cost estimates for direct air capture, which are around $600 to $1,000 per metric ton. Being able to sell electricity helps bring those costs down, but so does using plants to do the hard work of carbon removal.
Arbor’s — and BiCRS’ — biggest challenge is finding sustainable and equitable sources of biomass that don’t break the carbon budget. If the biomass has to travel too far or if harvesting it degrades an ecosystem too much, it eats into the total amount of carbon that ends up being removed.
Still, experts think there’s enough out there. Between agricultural and forest waste and fast-growing grasses grown on marginal lands, there’s likely enough biomass available to remove between 2.5 and 5 billion metric tons of CO2 every year by 2050.
BiCRS alone won’t be enough to claw back all the carbon released since the start of the Industrial Revolution, a whopping 2.4 trillion tons. But the technology could give companies like Arbor a quicker path to profitability.
Long-term, the challenge for Arbor and other carbon-removal companies is convincing the world that taking CO2 out of the atmosphere is a service worth paying for. It might be hard to imagine now, but sewage treatment, inconceivable 200 years ago, is commonplace today. As climate change grows more perilous, that argument in favor of carbon removal will only get easier.






























Comment