Miguel Fernandez
More posts from Miguel Fernandez
A few years ago, founders only had two options when starting a company — bootstrap yourself or turn to VC money, and they would use that money primarily to pursue growth. Later on, venture debt started to gain prominence. While non-dilutive, its problems are similar to that of VC equity: It takes time to secure, involves warrants, isn’t very flexible and not every startup can get it.
But in recent years, more options have become available to founders. Most startups can now avail non-dilutive capital, and purpose-specific financing has entered the fray.
While venture capital remains the most popular avenue for startups, founders should take advantage of all the financing options available to them. Using an optimal combination of capital sources means using cost-effective, short-term funding for imminent goals, and more expensive long-term money for activities with uncertain returns on the horizon.
What is revenue-based financing?
Let’s define it as capital provided based on future revenue.
So what is unique about revenue-based financing? Firstly, it is quick to raise. Compared with the months-long process usually involved with other forms of equity or debt financing, revenue-based financing can be set up in days or even hours. It is also flexible, meaning you don’t have to withdraw all the capital up front and choose to take it in chunks and deploy it over time.
Revenue-based financing also scales as your credit availability increases. Usually, there’s only one simple fee with fixed monthly repayments.
How should startups evolve their financing playbook?
To optimize fundraising using different sources of capital, startups should think about aligning short- and long-term activities with short- and long-term sources of funds. Revenue-based financing is shorter term in nature, and a typical term ranges between 12 and 24 months. Venture capital and venture debt are longer-term capital sources, with a typical term of two to four years.
A startup’s short-term activities may include marketing, sales, implementation and associated costs. If a startup knows its economics, CAC and LTV, it can predict how much revenue it will generate if it invests a certain amount in growth. Because the return on these activities may be higher than the cost of revenue-based financing, startups should use revenue-based financing to fund initiatives that will bear fruit soon.
On the other hand, long-term capital should be used for initiatives that will take time, such as major product development, R&D, expansion into new geographies and M&A. These are all bets with uncertain returns and uncertain timings that should be funded through venture equity or debt, because if the bets don’t work out, a company will have time to figure things out.
For example, consider a best-in-class SaaS company with an established go-to-market strategy. Through revenue-based financing, this company can use between 20% and 60% of its annual recurring revenue (ARR) to invest in growth. If this company has ARR of $2 million and receives a financing offer for $800,000 (40% of ARR), it can choose to withdraw $200,000 to invest in growth and add an additional ARR of $200,000 in the next few months.
Because revenue-based financing scales with ARR growth, the company can now access even more financing ($880,000 would be 40% of $2.4 million in ARR) to further invest in top-line growth.
This is how revenue-based financing can create a circular motion effect that lets a startup grow faster without using VC money. The faster the company grows, the more money it has to invest in increasing its revenue. Based on our own proprietary data, we have seen companies growing 50%-60% faster after using revenue-based financing.
Let’s take a look at an example of how a SaaS company can use revenue-based financing to finance its customer acquisition costs. This enterprise business sells relatively large contracts that average $10,000 per month (or $120,000 annually). Whenever this business signs new deals, they incur various costs.
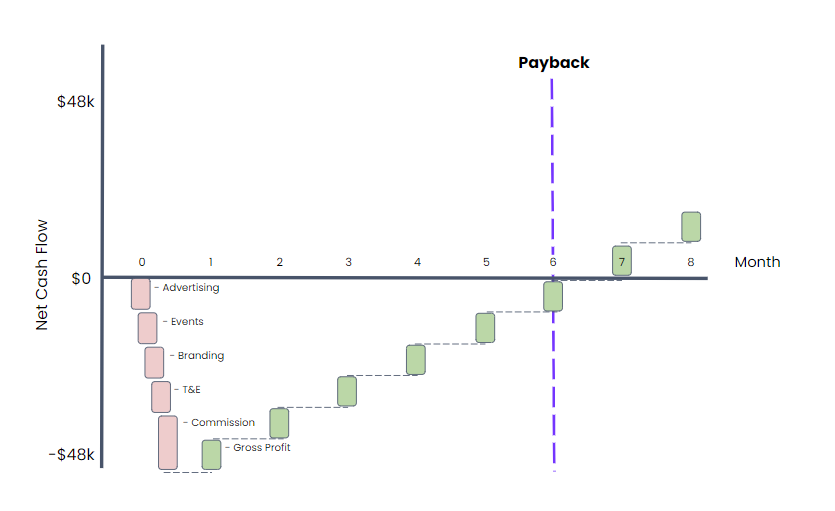
Let’s first think about ongoing costs and assume $2,000 in cost of goods sold. Next to consider are all the costs that go into acquiring a customer: ads, events, branding, payroll, sales, etc. Let’s assume these costs add up to $38,000. Finally, the business also incurs post-close expenses, say hardware costs and sales commissions, and let’s assume they add up to $10,000. So before acquiring a customer, this SaaS business incurs $48,000 in costs right away.
Assuming this company has payment terms of 30 days (in reality, this could be even longer), in the first month, it has to spend $48,000 to acquire a customer and it doesn’t collect the money until a month later. Since the company is making $8,000 in gross profit, however, the payback period would be six months.
Using revenue-based financing, this company can finance this short-term problem. The company can draw $48,000 (its CAC). Assuming 9.4% cost of financing, its gets $43,500 net on a six-month term (to match the payback period), which means that it can repay $8,000 per month. This lets the company spend only $4,500 to acquire a customer (versus $48,000 without revenue-based financing).
Any SaaS business wants to acquire as many customers per month as possible. If this company won five new contracts, its cash needs will rise to $240,000, and if it were to acquire 25 customers, it will need $1.2 million. Revenue-based financing can solve this working capital problem.
Here’s an illustration of our example startup’s growth if it financed its own growth:
And here’s what its growth would look like if it opted for revenue-based financing:
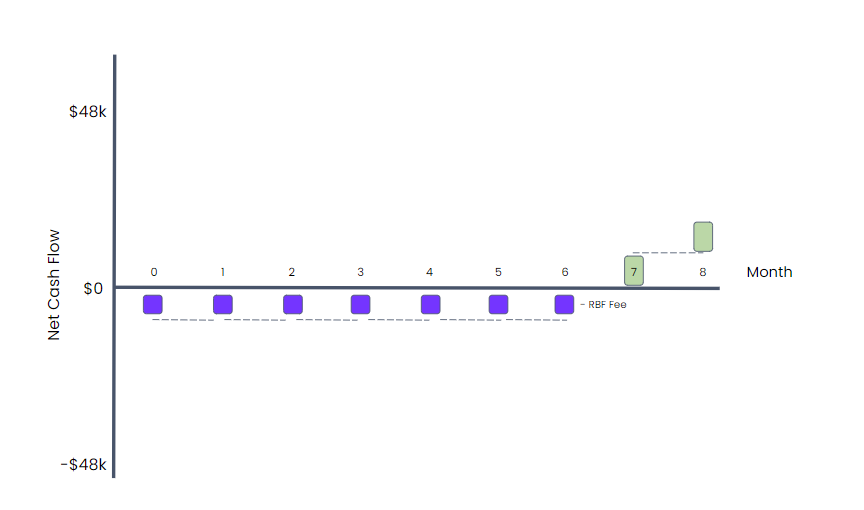
When using revenue-based financing, a startup should only draw the amount of money that it plans to put to work so it avoids paying for capital that is not generating returns. This would require the startup to make smaller withdrawals at frequent intervals and invest directly in activities that have higher returns than the cost of capital.
SaaS companies typically spend about 45% of their revenue on growth activities such as marketing and sales, and the remaining 55% in other areas. Using long-term capital for just 55% of those other investments and funding growth through non-dilutive capital can therefore extend a company’s runway and result in faster growth.
The ongoing market uncertainty has only increased the importance of additional sources of capital in a startup’s capital stack. This environment will show founders that there are complementary options available to fund their operations and scale reliably rather than relying solely on venture capital.































Comment