We’ve been shipping things across the oceans for centuries, and the world’s supply chains increasingly rely on diesel-powered megaships big enough to block entire channels by themselves. How do you decarbonize this monolithic industry? Fleetzero thinks it can with electric vessels making short hops all the way around the Pacific, while relying on smaller ports and a clever battery-sharing scheme.
This problem is a serious one for anyone looking at emissions and impact on the climate and oceans, as these huge ships carry a large proportion of the world’s cargo and emit on the order of a billion tons of carbon per year. There’s a lot of opportunity here, but like other legacy industries — and indeed the ships themselves — it can be difficult to overcome inertia.
Steven Henderson and Mike Carter grew up in and around the shipping world and, as engineers, they understand the immense forces and challenges at play for anyone looking to change how the industry works. Electrifying a consumer vehicle is a cakewalk compared with converting a thousand-foot ship with an engine the size of a building. And even if you manage to do it, how are you going to recharge — run out a dozen extension cords to the base of a crane every hundred miles?
It’s a conglomeration of serious problems on both the engineering and logistical sides, and the industry has been paralyzed by the assumption that moving away from the dirty traditional methods would be both complex and costly. With margins already being eaten into by a variety of things (including, now, skyrocketing gas costs), can they really afford to take on the expense of shifting to more sustainable propulsion? An increase in costs, unwelcome even to successful shippers, could put smaller and less wealthy regions and companies out of the game entirely.
Fortunately, Fleetzero believes that its solution will not only be cleaner, but cheaper to operate. The reasons for this start with the surprising (to lubbers) fact that transoceanic shipping doesn’t necessarily just go “straight” across the ocean; from Eastern Asia to West Coast ports, it’s almost as direct (and potentially less risky) to follow the coast much of the way. It looks much longer but due to the curvature of the Earth it’s actually not — and you have the benefit of being close to land to resupply or make deliveries on the way.
If you don’t have to travel several thousand miles uninterrupted, battery-powered shipping starts to make a lot more sense, and actually it’s just one of several puzzle pieces that fit together to form a potentially transformative picture.
Standard shipping units
“The weird economics of this is that the more ships you have, and the more stops you have, the lower your cost is. The key is to make the batteries swappable — this wouldn’t work for a plug-in vessel,” said Henderson.
It’s a bit counterintuitive — “I actually had to model this out on the floor with my daughter’s toy boats,” he added — but think about it this way: If a ship has enough batteries to go a thousand miles, then unless you’re going exactly that distance every time, you either have too much or too little capacity. And if you only have one large ship that has to swap out batteries at each end, you must keep twice the number of active batteries around — a set to swap out at each destination. But if you split the same capacity among several smaller ships and add more possible stops, suddenly it takes far less battery capacity to move the same amount of cargo.
This helpful diagram of a simple case may help make it clear:
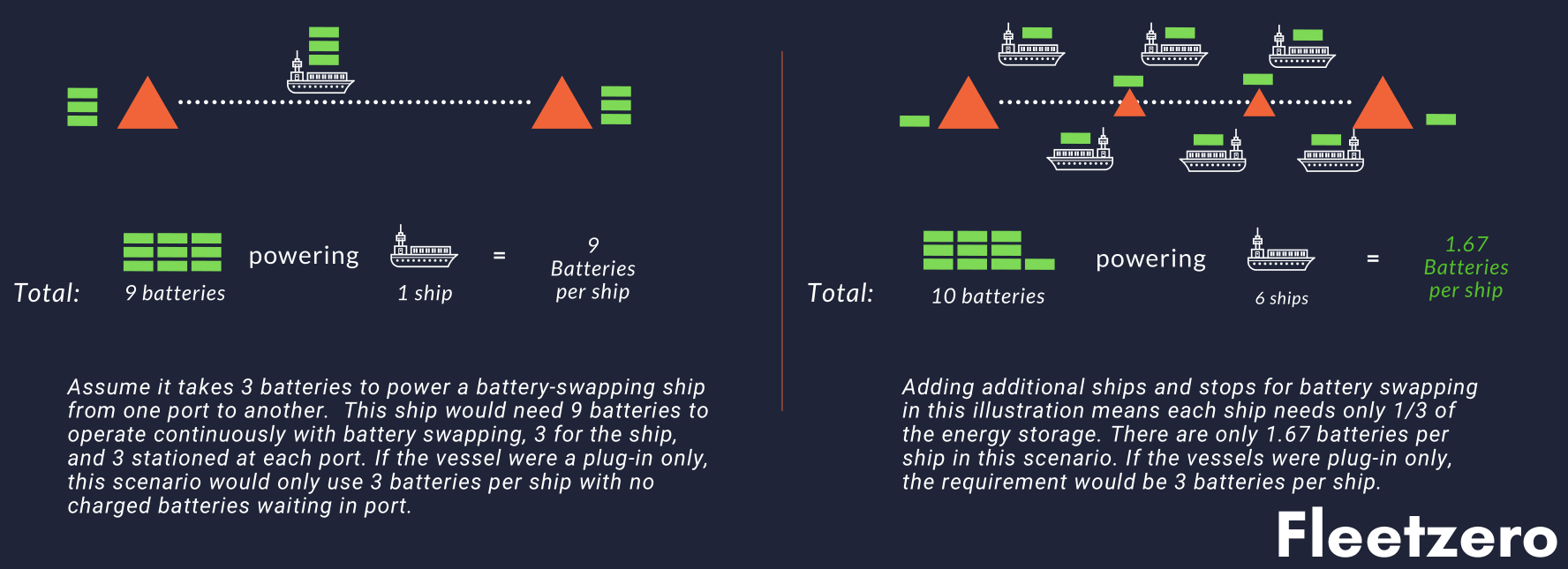
There are plenty more configurations in between, but the idea is clear enough: more and smaller ships use fewer batteries to move the same amount of cargo, assuming you have intermediate ports to make the swap network flexible. Plug-in vessels won’t work partly because they carry a lot of batteries (leading to under-utilization), but also because dockside charging may not be available.
Since batteries are the most expensive part of electrifying a ship, efficiency lowers the fleet buy-in cost by a huge amount. But of course this approach also requires charging infrastructure at ports that may not have it. Fleetzero’s approach, which seems obvious in retrospect, is to make the ship’s batteries as portable as its cargo — by putting them in shipping containers.
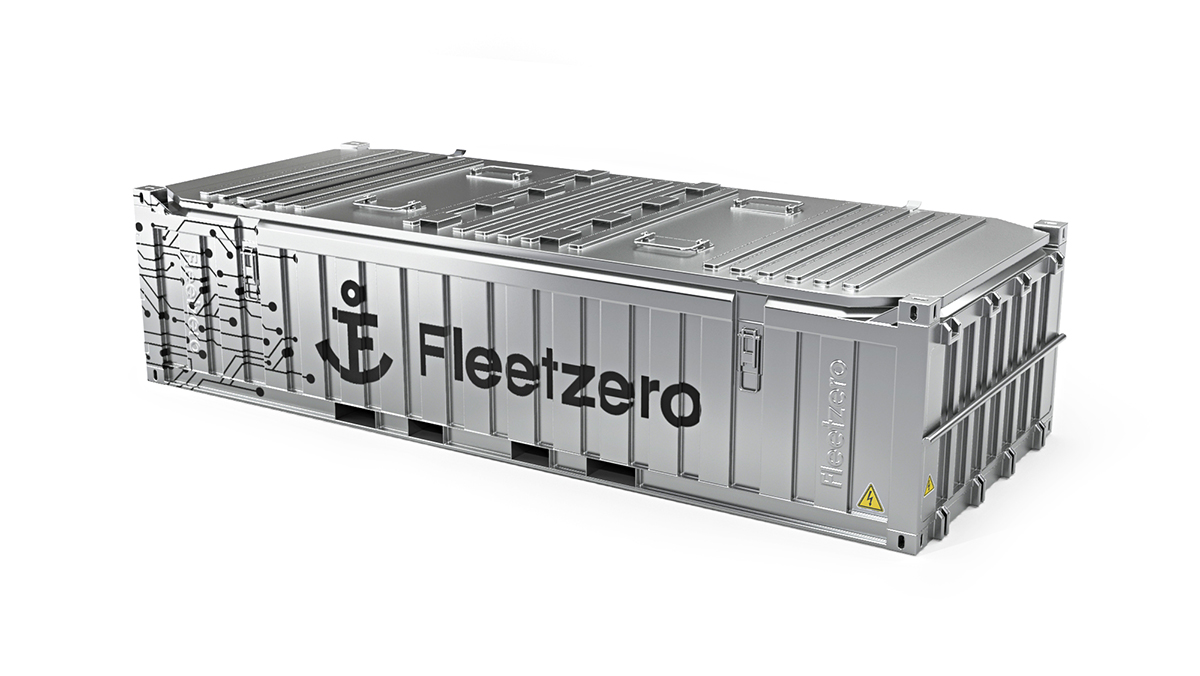

In case you’re thinking these will take up a lot of space, there are two answers to that. First, by removing the huge diesel engines and fuel and ballast tanks, you open up a ton of space on any given ship, sometimes doubling cargo capacity. And second, you only have to take as many as you need.
“We can put two batteries on a ship or two hundred, changing the range every time we load it out,” said Henderson. “You unload and load them just like any other cargo; it gets taken where it needs to go, a warehouse or a local utility.”
There, they can take advantage of off-peak electricity to charge these Leviathan batteries (as they call them) cheaply, or even be used as temporary power for ships to plug into so they don’t have to run on their own diesel generators.
“Electrifying docks is expensive — all these ports are 50, 100 years old,” Henderson continued. “It was actually pitched back to us that it’s cheaper to use our batteries to power other ships, that way you don’t have to build a substation at every dock.”
This feeds into the next puzzle piece — fitting this hypothetical network of ships to a real network of ports.
Ports of call
Carter explained that when they were spitballing the idea, it was clear that a direct shot across the ocean on a 10,000-container megaship would require a battery stack a couple miles tall — something of an engineering challenge — and while ships that hold only a handful of containers could do it, the logistics or a swarm of small vessels didn’t work out. “There’s a sweet spot for the size of ship you want to use, and it’s about a three to four thousand container unit ship,” he said. (The images in this article are of a proposed smaller test ship.)
“Because they’re on the smaller side — we’re still talking about 700 feet — you can access smaller ports,” Carter said. “There are all these ports, but no vessels that fit into them. Being able to use smaller vessels gives [logistics companies] so much more flexibility in the supply chain than they have today. If we look at places like Portland or Everett, these are ports not a lot of people know about, but there’s not as much congestion, and we can get cargo closer to the customers.”
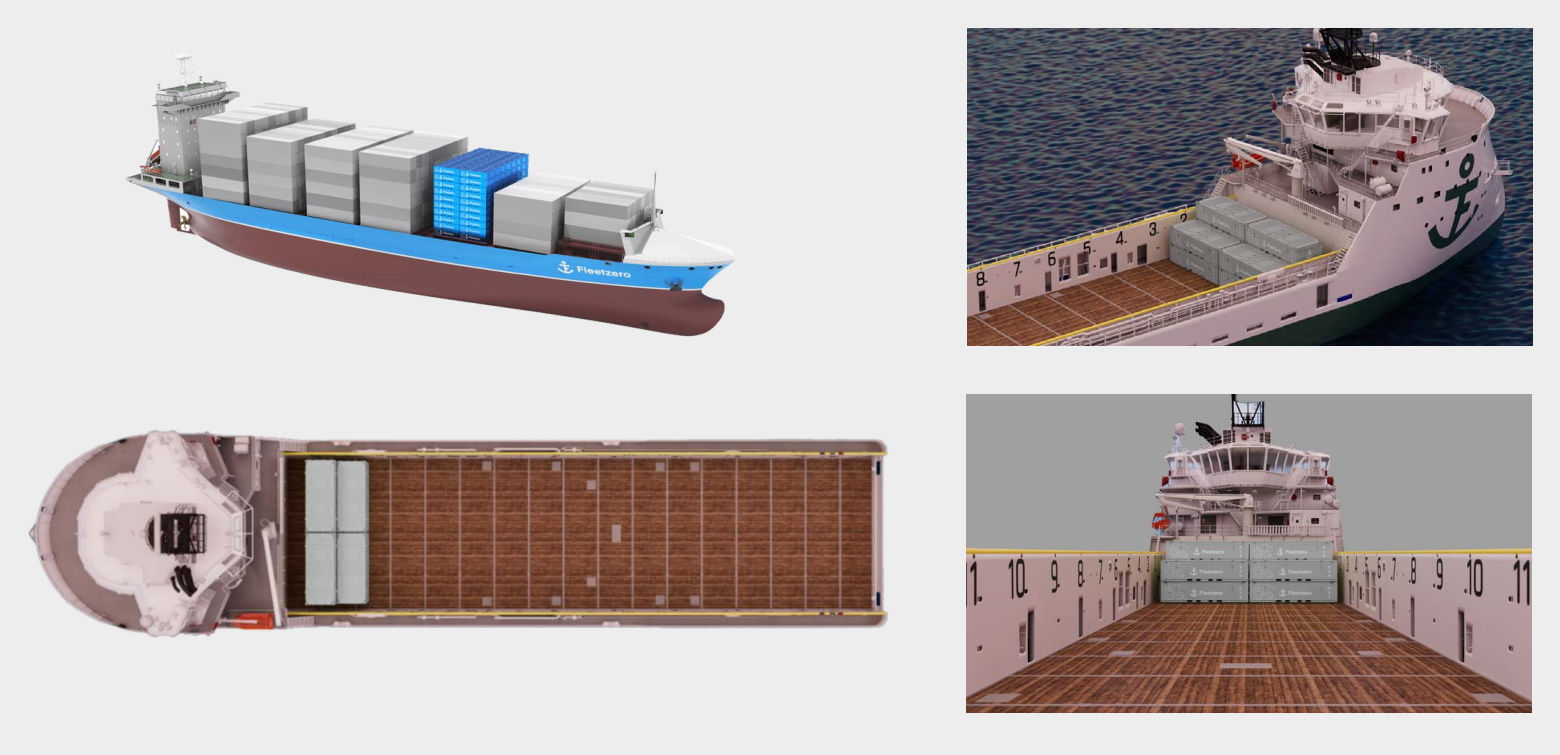

This also enables the idea of having frequent pit stops for ships where they can drop off depleted batteries and pick up just enough new ones to get them to their destination, like building a network of charging stations along highways. The local governments and port managers at these smaller locations are, perhaps needless to say, enthusiastic about the idea of bringing in new and regular business.
So: Using portable, container-sized batteries makes medium-distance travel in medium-size ships practical, which activates smaller ports, which can act as charging stations without too much investment, reinforcing the network and driving the cost of fleet operations down — making battery-powered shipping competitive with and perhaps even cheaper than traditional gas-driven vessels.
It sounds promising, but it also sounds like a lot. Like any sensible startup, they’re starting small, proving the concept, and will be ready to scale within three years. While they’re just making their debut at Y Combinator’s Demo Day in the latest winter cohort, Fleetzero has already raised $3.5 million in a combination of angel and pre-seed rounds. Investors include Sam Altman, John Doerr, David Rubenstein, David Adelman, Flexport, Y Combinator, My Climate Journey and Joris Poort.
The first task was to build the batteries, which they noted have a very different chemistry from most you’d find out there, largely due to the extreme danger posed by fires on these ships. “We needed a battery that didn’t self oxidize,” said Henderson, referring to the process that can make things like lithium ion and nickel metal hydride batteries serious risks. They ended up going with lithium iron phosphate, and building in both passive and active fire suppression measures.
That settled, their next task is to load a bunch on the back of a 300-foot ship and test out the whole shipping and swapping process start to finish. When that’s done and they’ve obtained the required regulatory approvals, they’ll begin converting vessels in 2025 — all after raising more money, presumably.
With luck and a lot of work, Fleetzero could begin commercial operations that same year. Although it’s a lot to bite off, they have the advantage of having pretty much everyone rooting for them — electrifying shipping at this scale would benefit fleet owners, port operators, logistics companies and, last but not least, the planet.






























Comment