AI is fundamental to many products and services today, but its hunger for data and computing cycles is bottomless. Lightmatter plans to leapfrog Moore’s law with its ultra-fast photonic chips specialized for AI work, and with a new $80 million round, the company is poised to take its light-powered computing to market.
We first covered Lightmatter in 2018, when the founders were fresh out of MIT and had raised $11 million to prove that their idea of photonic computing was as valuable as they claimed. They spent the next three years and change building and refining the tech — and running into all the hurdles that hardware startups and technical founders tend to find.
For a full breakdown of what the company’s tech does, read that feature — the essentials haven’t changed.
Lightmatter aims to reinvent AI-specific chips with photonic computing and $11M in funding
In a nutshell, Lightmatter’s chips perform in a flash — literally — certain complex calculations fundamental to machine learning. Instead of using charge, logic gates and transistors to record and manipulate data, the chips use photonic circuits that perform the calculations by manipulating the path of light. It’s been possible for years, but until recently getting it to work at scale, and for a practical, indeed a highly valuable purpose, has not.
Prototype to product
It wasn’t entirely clear in 2018 when Lightmatter was getting off the ground whether this tech would be something they could sell to replace more traditional compute clusters like the thousands of custom units companies like Google and Amazon use to train their AIs.
“We knew in principle the tech should be great, but there were a lot of details we needed to figure out,” CEO and co-founder Nick Harris told TechCrunch in an interview. “Lots of hard theoretical computer science and chip design challenges we needed to overcome… and COVID was a beast.”
With suppliers out of commission and many in the industry pausing partnerships, delaying projects and other things, the pandemic put Lightmatter months behind schedule, but they came out the other side stronger. Harris said that the challenges of building a chip company from the ground up were substantial, if not unexpected.

“In general what we’re doing is pretty crazy,” he admitted. “We’re building computers from nothing. We design the chip, the chip package, the card the chip package sits on, the system the cards go in, and the software that runs on it…. we’ve had to build a company that straddles all this expertise.”
That company has grown from its handful of founders to more than 70 employees in Mountain View and Boston, and the growth will continue as it brings its new product to market.
Where a few years ago Lightmatter’s product was more of a well-informed twinkle in the eye, now it has taken a more solid form in the Envise, which they call a “general-purpose photonic AI accelerator.” It’s a server unit designed to fit into normal data center racks but equipped with multiple photonic computing units, which can perform neural network inference processes at mind-boggling speeds. (It’s limited to certain types of calculations, namely linear algebra for now, and not complex logic, but this type of math happens to be a major component of machine learning processes.)
Harris was reticent to provide exact numbers on performance improvements, but more because those improvements are increasing than that they’re not impressive enough. The website suggests it’s 5x faster than an Nvidia A100 unit on a large transformer model like BERT, while using about 15% of the energy. That makes the platform doubly attractive to deep-pocketed AI giants like Google and Amazon, which constantly require both more computing power and who pay through the nose for the energy required to use it. Either better performance or lower energy cost would be great — both together is irresistible.
It’s Lightmatter’s initial plan to test these units with its most likely customers by the end of 2021, refining it and bringing it up to production levels so it can be sold widely. But Harris emphasized this was essentially the Model T of their new approach.
“If we’re right, we just invented the next transistor,” he said, and for the purposes of large-scale computing, the claim is not without merit. You’re not going to have a miniature photonic computer in your hand any time soon, but in data centers, where as much as 10% of the world’s power is predicted to go by 2030, “they really have unlimited appetite.”
The color of math
There are two main ways by which Lightmatter plans to improve the capabilities of its photonic computers. The first, and most insane-sounding, is processing in different colors.
It’s not so wild when you think about how these computers actually work. Transistors, which have been at the heart of computing for decades, use electricity to perform logic operations, opening and closing gates and so on. At a macro scale you can have different frequencies of electricity that can be manipulated like waveforms, but at this smaller scale it doesn’t work like that. You just have one form of currency, electrons, and gates are either open or closed.
In Lightmatter’s devices, however, light passes through waveguides that perform the calculations as it goes, simplifying (in some ways) and speeding up the process. And light, as we all learned in science class, comes in a variety of wavelengths — all of which can be used independently and simultaneously on the same hardware.
The same optical magic that lets a signal sent from a blue laser be processed at the speed of light works for a red or a green laser with minimal modification. And if the light waves don’t interfere with one another, they can travel through the same optical components at the same time without losing any coherence.
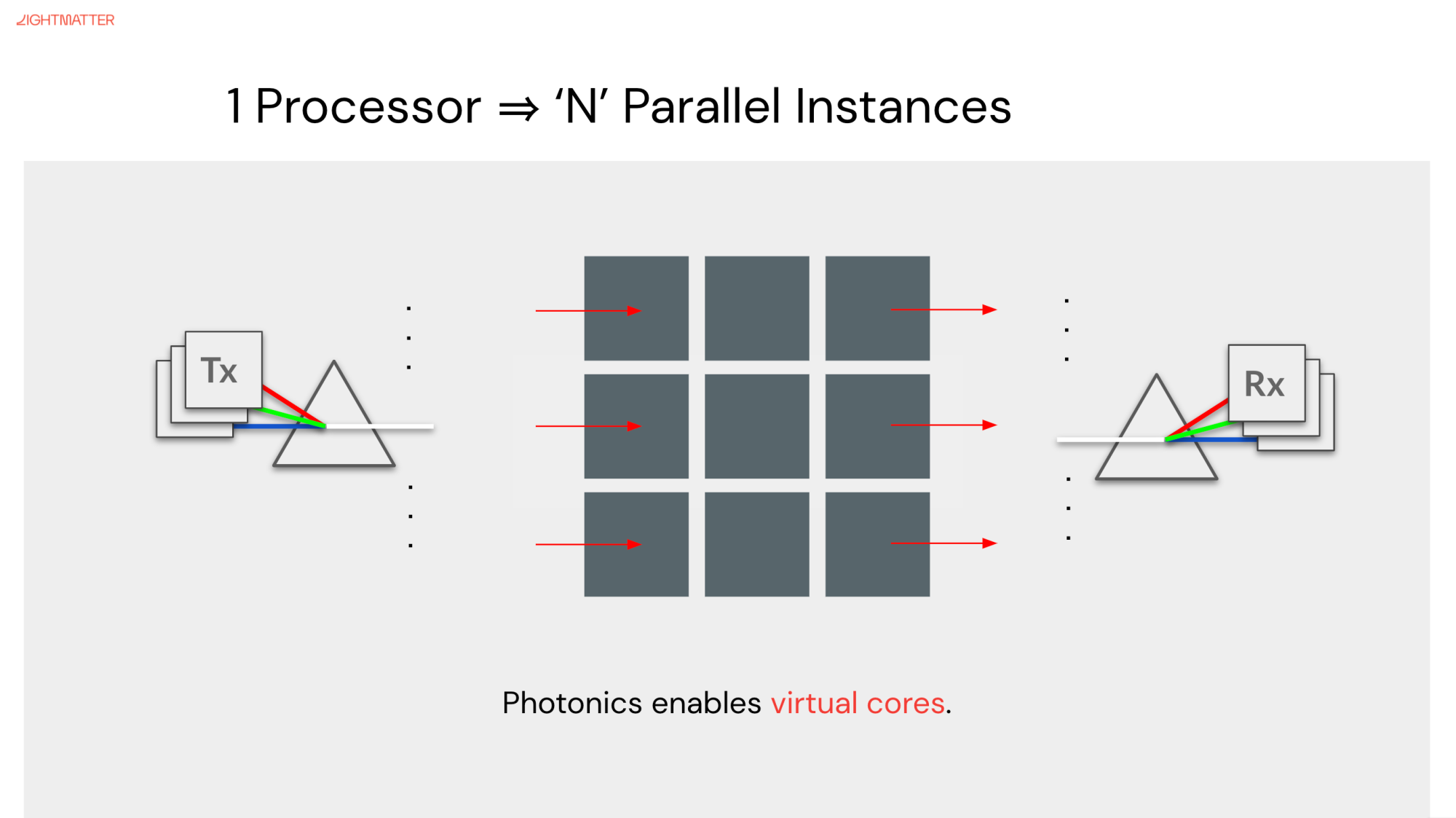
That means that if a Lightmatter chip can do, say, a million calculations a second using a red laser source, adding another color doubles that to two million, adding another makes three — with very little in the way of modification needed. The chief obstacle is getting lasers that are up to the task, Harris said. Being able to take roughly the same hardware and near-instantly double, triple or 20x the performance makes for a nice roadmap.
It also leads to the second challenge the company is working on clearing away, namely interconnect. Any supercomputer is composed of many small individual computers, thousands and thousands of them, working in perfect synchrony. In order for them to do so, they need to communicate constantly to make sure each core knows what other cores are doing, and otherwise coordinate the immensely complex computing problems supercomputing is designed to take on. (Intel talks about this “concurrency” problem building an exa-scale supercomputer here.)
Intel and Argonne National Lab on ‘exascale’ and their new Aurora supercomputer
“One of the things we’ve learned along the way is, how do you get these chips to talk to each other when they get to the point where they’re so fast that they’re just sitting there waiting most of the time?” said Harris. The Lightmatter chips are doing work so quickly that they can’t rely on traditional computing cores to coordinate between them.
A photonic problem, it seems, requires a photonic solution: a wafer-scale interconnect board that uses waveguides instead of fiber optics to transfer data between the different cores. Fiber connections aren’t exactly slow, of course, but they aren’t infinitely fast, and the fibers themselves are actually fairly bulky at the scales chips are designed, limiting the number of channels you can have between cores.
“We built the optics, the waveguides, into the chip itself; we can fit 40 waveguides into the space of a single optical fiber,” said Harris. “That means you have way more lanes operating in parallel — it gets you to absurdly high interconnect speeds.” (Chip and server fiends can find that specs here.)
The optical interconnect board is called Passage, and will be part of a future generation of its Envise products — but as with the color calculation, it’s for a future generation. Five-10x performance at a fraction of the power will have to satisfy their potential customers for the present.
Putting that $80M to work
Those customers, initially the “hyper-scale” data handlers that already own data centers and supercomputers that they’re maxing out, will be getting the first test chips later this year. That’s where the B round is primarily going, Harris said: “We’re funding our early access program.”
That means both building hardware to ship (very expensive per unit before economies of scale kick in, not to mention the present difficulties with suppliers) and building the go-to-market team. Servicing, support and the immense amount of software that goes along with something like this — there’s a lot of hiring going on.
The round itself was led by Viking Global Investors, with participation from HP Enterprise, Lockheed Martin, SIP Global Partners, and previous investors GV, Matrix Partners and Spark Capital. It brings their total raised to about $113 million; There was the initial $11 million A round, then GV hopping on with a $22 million A-1, then this $80 million.
Although there are other companies pursuing photonic computing and its potential applications in neural networks especially, Harris didn’t seem to feel that they were nipping at Lightmatter’s heels. Few if any seem close to shipping a product, and at any rate this is a market that is in the middle of its hockey stick moment. He pointed to an OpenAI study indicating that the demand for AI-related computing is increasing far faster than existing technology can provide it, except with ever larger data centers.
The next decade will bring economic and political pressure to rein in that power consumption, just as we’ve seen with the cryptocurrency world, and Lightmatter is poised and ready to provide an efficient, powerful alternative to the usual GPU-based fare.
As Harris suggested hopefully earlier, what his company has made is potentially transformative in the industry, and if so there’s no hurry — if there’s a gold rush, they’ve already staked their claim.
Quantum photonics startup Nu Quantum raises £2.1M from Amadeus Capital Partners






























Comment