A week after Facebook grabbed eyeballs globally by blocking news publishers and turning off news-sharing on its platform in Australia, the country’s parliament has approved legislation that makes it mandatory for platform giants like Facebook and Google to negotiate to remunerate local news publishers for their content, to take account of how journalism is shared on their platforms.
The News Media and Digital Platforms Mandatory Bargaining Code was developed in conjunction with Australia’s Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) with the aim of addressing the power imbalance that exists between digital platforms and news businesses.
Australia now has a template for forcing Facebook and Google to pay for news
Facebook and Google had both lobbied aggressively against the legislation, with Google initially threatening to close down its search engine in Australia — before changing tack and hurrying to strike deals with local publishers in a bid to undercut the law by showing an alternative model.
But none of the tech giants’ moves derailed the legislative effort entirely.
“The Code will ensure that news media businesses are fairly remunerated for the content they generate, helping to sustain public interest journalism in Australia,” said treasury minister Josh Frydenberg and communications minister Paul Fletcher in a joint statement today.
“The Code provides a framework for good faith negotiations between the parties and a fair and balanced arbitration process to resolve outstanding disputes,” they added.
The Morrison Government’s world-leading news media bargaining code has just passed the Parliament.
This is a significant milestone.
This legislation will help level the playing field & see Australian news media businesses paid for generating original content. @PaulFletcherMP pic.twitter.com/33bQbiqeMI
— Josh Frydenberg (@JoshFrydenberg) February 24, 2021
The operation of the code will be reviewed by the government within a year “to ensure it is delivering outcomes that are consistent with the Government’s policy intent”, they added.
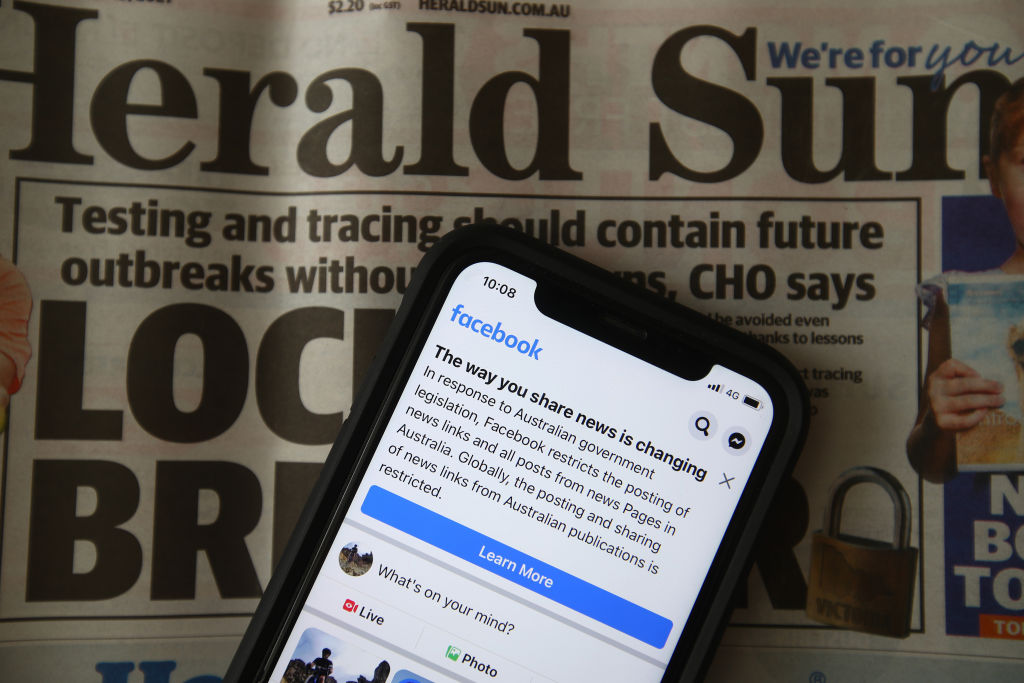
On Tuesday Facebook reversed course on its intentionally over-broad news ban after the government agreed to make amendments to the draft legislation — including adding a two-month mediation period to allow digital platforms and publishers to agree to deals before being forced to enter into arbitration.
The government also agreed to take platforms’ existing deals with publishers into account before deciding whether the code applies to them and provide them with one month’s notice before taking a final decision.
Facebook said it was satisfied with the tweaks, having been concerned commercial deals it struck off its own bat would not be taken into account.
In a blog post which the tech giant entitled “the real story” (yes, really), Facebook’s chief spin doctor, Nick Clegg — aka the former deputy prime minister of the U.K. — wrote that the law as originally drafted would have forced it to pay “potentially unlimited amounts of money to multi-national media conglomerates under an arbitration system that deliberately misdescribes the relationship between publishers and Facebook”.
“Thankfully, after further discussion, the Australian government has agreed to changes that mean fair negotiations are encouraged without the looming threat of heavy-handed and unpredictable arbitration,” Clegg added.
Who exactly has come out on top in this stand-off between a sovereign government and two of the biggest tech giants in the world remains to be seen. But if Facebook and Google were hoping to block the law they certainly failed.
Claims by the Australian government that public interest journalism has won are, however, being tempered by critical suggestions that the law will merely end up favoring big media over small publishers — after all, it’s the larger publishers Google has rushed to strike deals with, for example.
How much of the adtech duopoly’s money ends up trickling down to support smaller publishers and grow media pluralism in Australia isn’t yet clear. But the suspicion among some is that the whole episode amounts to a shakedown of big tech by big media via their friends in government — and that ugly oligarchy won.
There is also the risk that by directly linking the funding of public interest journalism — and therefore, by implication, the vitality of a country’s democracy — to tech giants like Facebook and Google it will further entrench the monopoly positions of those selfsame giants.
Suddenly calls to break up Google et al. can be conflated with “harming democracy” by taking money away from “public interest journalism”. Even just the claim of support suggests rich PR pickings for Facebook and co.
Yet these are platform giants that already have massive and unprecedented power over the public information sphere — as Facebook just demonstrated, via its flex against legislators (showing it can flip a switch to crater traffic to all sorts of publicly valuable information if it so chooses, leaving all its users in an entire country vulnerable to disinformation).
Facebook applies overly broad content block in flex against Australia’s planned news reuse law
Their dominance has also long been implicated in harming democracy around the world — as their ad-funded business models profile people and amplify content for profit, without any kind of public service mission (quite unlike traditional media).
So if the tech giants were looking for a cheap way to reduce their antitrust risk, then paying over a couple of billion every few years to regional publishers (who they may hope will also dial down their techlash rhetoric as a result) probably doesn’t sound so bad.
Facebook said this week that it plans to spend at least $1 billion on “supporting” the news media over the next three years. Google also recently outed a $1 billion fund for news licensing fees.
Neither company can claim it just discovered the existence of journalism; it’s crystal clear these suddenly pledged billions are only on the table because lawmakers have made platforms paying for news mandatory. (Australia is not alone here; EU lawmakers also legislated in recent years to extend copyright to cover snippets of news — which is starting to result in Google striking licensing deals with publishers in Europe.)
So news publishers are certainly winning by gaining revenue that wasn’t being made available to them before. Though at what wider cost — if the mechanism being used to support them helps entrench anti-democratic monopolists?
The lack of transparency around the commercial deals being struck between platforms and publishers is certainly unhelpful. Without clarity on such arrangements the risk, again, is that the law will favor the big publishers while the smaller ones (who may have more of a public interest mission) will be at a disadvantage — needing to work even harder to compete with tabloid giants further fattened up with fresh adtech profits.
Australia has for certain won something, though. It’s bagged the world’s attention for taking on tech giants through a legislative code.
Its direct thrust at Facebook and Google — coming up with a framework tailor made to take on their market power — has caught the eye of other policymakers and competition regulators.
The chief of the U.K.’s Competition and Markets Authority, Andrea Coscelli, said this week that he’s watching the media code with interest as the U.K. government moves at a clip to set up a pro-competition regulator with the aim of reining in big tech, calling Australia’s approach of having a backstop of mandatory arbitration if commercial negotiations fail “a sensible one”.
“We are definitely following what’s happening in Australia,” he told the BBC. “We think they are dealing with problems we have in the U.K. as well and they are coming up with possible solutions to that. There are many variants to it but certainly I think it’s a very important data point for what we could do in the U.K.”
Asked if the U.K. should follow Australia’s example, Coscelli gave a cautious thumbs up to something along those lines, saying: “We have said we should also think about fair trading between publishers and the platforms for news content. So I know both government and parliament is certainly interested in what’s happening in Australia — and potentially thinking about something similar.”
Facebook restricts users in Australia from sharing or viewing news links
Google threatens to close its search engine in Australia as it lobbies against digital news code






























Comment