Analysis of a trove of data extracted from the Chicago Police Department has revealed major differences between how Black and white officers, as well as male and female ones, actually enforce the law. This rare apples-to-apples comparison supports the idea that improving diversity in law enforcement may also improve the quality of policing.
Historically hard data from police departments has been extremely hard to come by, for a variety of reasons. As the authors put it in the paper:
Rigorous evaluation of the effects of police diversity has been stymied by a lack of sufficiently fine-grained data on officer deployment and behavior that makes it difficult or impossible to ensure that officers being compared are facing common circumstances while on duty.
… At present, a patchwork of nonstandard record-keeping and disclosure practices across roughly 18,000 U.S. police agencies has severely impeded broader policy evaluation.
This study by B.A. Ba et al., however, is based on highly detailed CPD records resulting from requests made to the department over a period of three years. It’s a collaboration between researchers from UC Irvine, the University of Pennsylvania, Princeton, and Columbia, and was published today in Science (access is free).
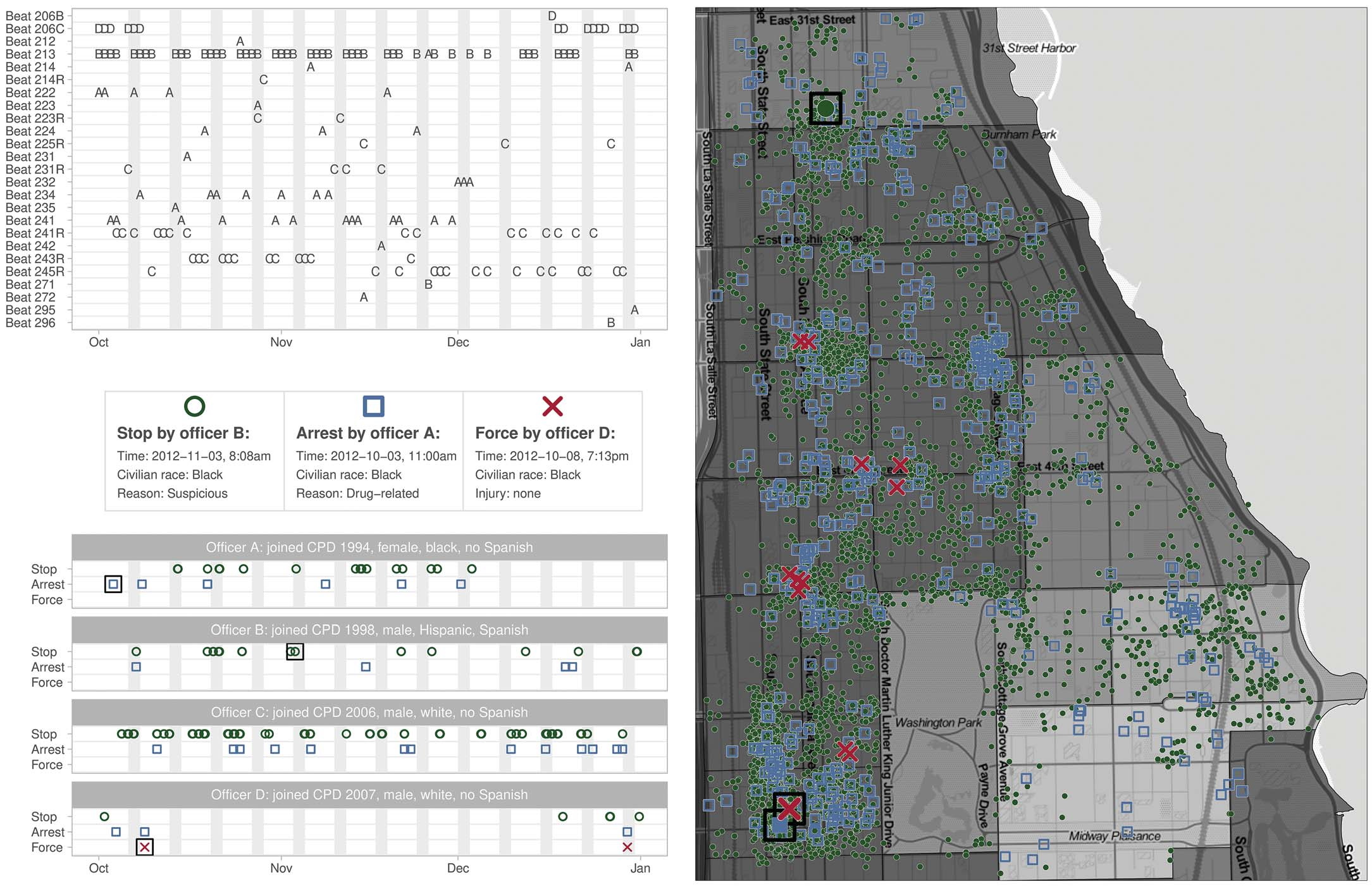
The records include millions of shifts and patrols from 2012 through 2015, which the team carefully sorted and pruned until it had a set that would allow the kind of analysis they hoped to do: comparing police work that is similar in all respects except the demographics of the officers doing it.
If on a Monday in March, in the same district at the same time of day, no serious differences could be found between Black officers and white officers, then race could be tentatively ruled out as a major contributor to how police do their work. On the other hand, if there were serious differences found, then that might indicate — as a topic for further study — the possibility of systemic bias of some kind.
Does tech have the guts to deploy its resources against police brutality?
As you might expect, the analysis found that there are indeed serious differences that, having isolated all the other variables, only correlate with the race of the officer. This may seem obvious to some and controversial to others, but the point of this work is not to assume or confirm assumptions, but to show plainly with data that there are disparities associated with race that need investigation and explanation.
Some of the specific findings can be summarized as follows:
- Minority officers (Black and Hispanic, self-identified) “receive vastly different patrol assignments,” something that had to be controlled for in order to provide effective comparisons for the other findings.
- Black officers use force 35% less than white officers on average, with most of the difference coming from force used against Black civilians.
- Black officers perform far fewer “discretionary stops” for “suspicious behavior.”
- Hispanic officers showed similar, but smaller reductions.
- Female officers use force considerably less often than male ones, again especially when it comes to Black civilians.
- Much of the disparity in stops, arrests and use of force results from differences in pursuing low-level offenses, especially in Black-majority neighborhoods.
The data show (as a sort of inverse image of the above list) that white male officers stop, arrest and use force more often, especially on people of color, and frequently as a result of minor crimes or “discretionary stops” with vague justifications.
The researchers are careful to point out that as conclusive as the patterns may appear to be, it’s important to understand that there is no causal mechanism studied or suggested. In fact they expressly point out that the data could be interpreted in two directions:
One explanation for these disparities centers on racial bias, i.e., white officers are more likely than Black officers to harass Black civilians. Technically, it is also possible that Black officers respond more leniently when observing crimes in progress.
More study is required, but they point out that one explanation — leniency by Black officers on minor offenses — has very little effect on public safety (violent crimes are addressed largely the same regardless of race and gender). The other — systemic racism — is significantly more harmful. Though they are “observationally equivalent” in the context of this data specifically, they are not equivalent in consequence. (Nor in likelihood — nor are they entirely incompatible with each other.)
Minneapolis police tapped Google to identify George Floyd protesters
In a valuable commentary on the paper and its implications, Yale’s Phillip Atiba Goff notes that its findings are rich in implications that we ignore at our peril:
The magnitude of the differences provides strong evidence that — at least in some cities — the number of officers who identify with vulnerable groups can matter quite a bit in predicting police behavior. Although this does not settle the matter, the work stands alone in its ability to make apples-to-apples comparisons across officers — regardless of how many may be bad apples.
Given that Ba et al. find negligible demographic differences in officers’ responses to community violence, such a large difference in discretionary stops compels a reader to ask: Are any of those excess stops by white officers necessary? Should a department even be making them, given the demonstrated risk for abuse so evident in vulnerable communities?
Are any of those excess use of force incidents by white officers necessary? And if the excess force is not necessary for public safety, why does the department target Black communities for so much physical coercion? These questions are difficult to answer outside a broader engagement with the purpose of policing — and its limitations.
In other words, while it may require further study to get at the core of these issues, police departments may look at them and find that their resources are not necessarily being used to best effect. Indeed they may have to face the possibility — if only to refute it — that much of what officers do has little, no, or even negative value to the community. As Goff concludes:
With violence trending downward the past three decades, mostly troubling small geographic areas, and possibly occupying a small portion of police activity, what should the role of police be? Failing to take seriously the possibility that the answer should be “much less” may end up frustrating both researchers and a public that has been asking the question for far longer than most scientists.
This revealing study was only possible because the authors and legal authorities in Chicago compelled the police there to release this data. As noted above it can be difficult, if it is even possible, to collect large-scale data from any department, let alone from many departments for analysis at a national scale. The authors freely admit that their findings, in their specificity to Chicago, may not apply equally in other cities.
But that’s meant to be a call to action; if when finally given access to real data, researchers find problems of this magnitude, every department in the country should be weighing the benefits and risks of continued obfuscation with those of openness and collaboration.
For Seattle’s cop-free protest zone, tech is both a revolutionary asset and disastrous liability






























Comment