Spyware maker NSO Group used real phone location data on thousands of unsuspecting people when it demonstrated its new COVID-19 contact-tracing system to governments and journalists, researchers have concluded.
NSO, a private intelligence company best known for developing and selling governments access to its Pegasus spyware, went on the charm offensive earlier this year to pitch its contact-tracing system, dubbed Fleming, aimed at helping governments track the spread of COVID-19. Fleming is designed to allow governments to feed location data from cell phone companies to visualize and track the spread of the virus. NSO gave several news outlets each a demo of Fleming, which NSO says helps governments make public health decisions “without compromising individual privacy.”
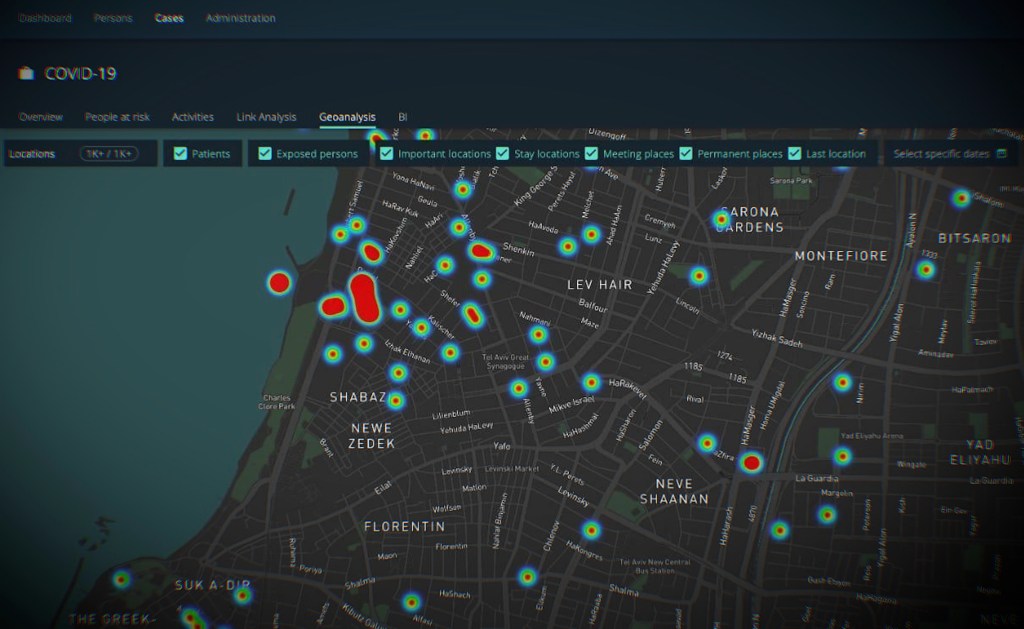
But in May, a security researcher told TechCrunch that he found an exposed database storing thousands of location data points used by NSO to demonstrate how Fleming works — the same demo seen by reporters weeks earlier.
TechCrunch reported the apparent security lapse to NSO, which quickly secured the database, but said that the location data was “not based on real and genuine data.”
NSO’s claim that the location data wasn’t real differed from reports in Israeli media, which said NSO had used phone location data obtained from advertising platforms, known as data brokers, to “train” the system. Academic and privacy expert Tehilla Shwartz Altshuler, who was also given a demo of Fleming, said NSO told her that the data was obtained from data brokers, which sell access to vast troves of aggregate location data collected from the apps installed on millions of phones.
TechCrunch asked researchers at Forensic Architecture, an academic unit at Goldsmiths, University of London that studies and examines human rights abuses, to investigate. The researchers published their findings on Wednesday, concluding that the exposed data was likely based on real phone location data.
The researchers said if the data is real, then NSO “violated the privacy” of 32,000 individuals across Rwanda, Israel, Bahrain, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates — countries that are reportedly customers of NSO’s spyware.
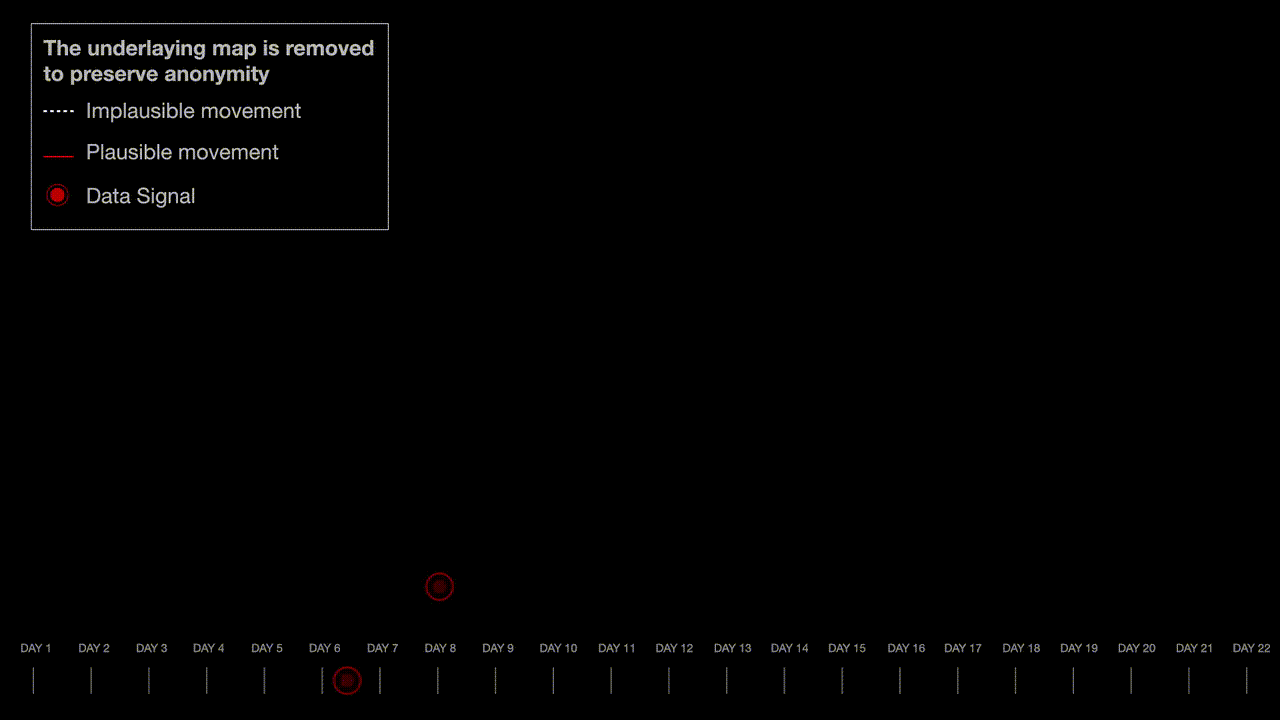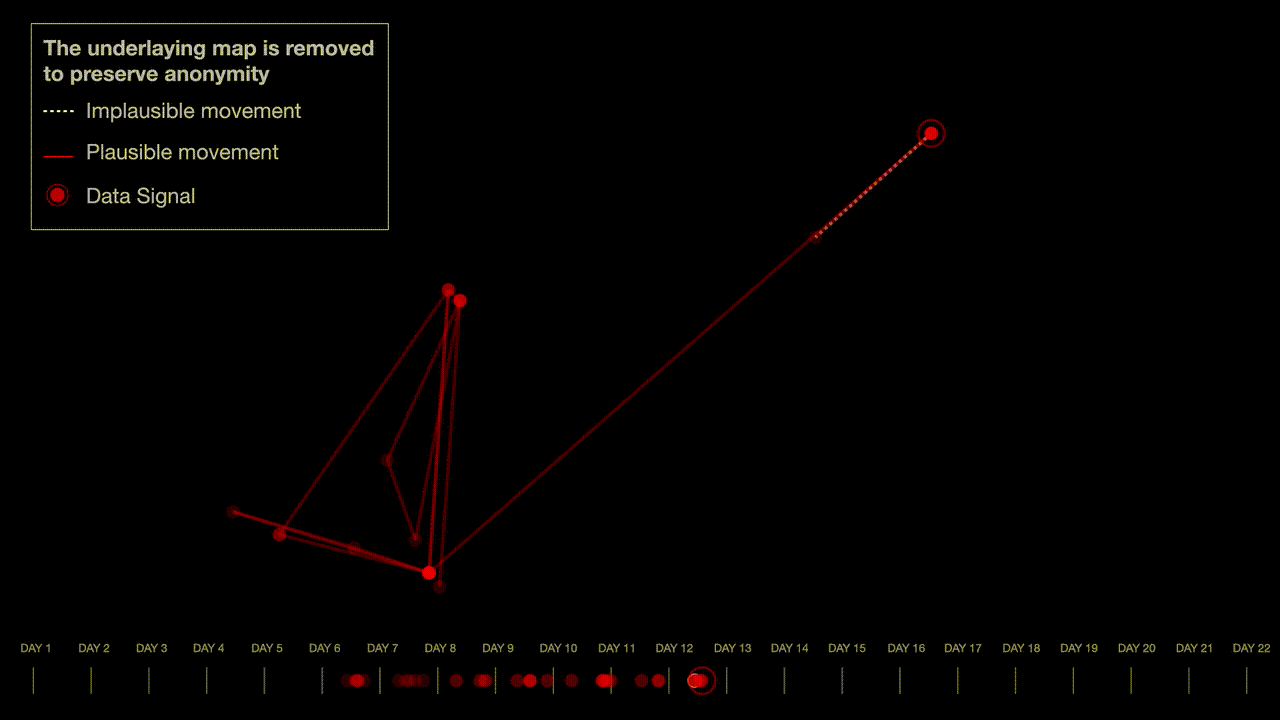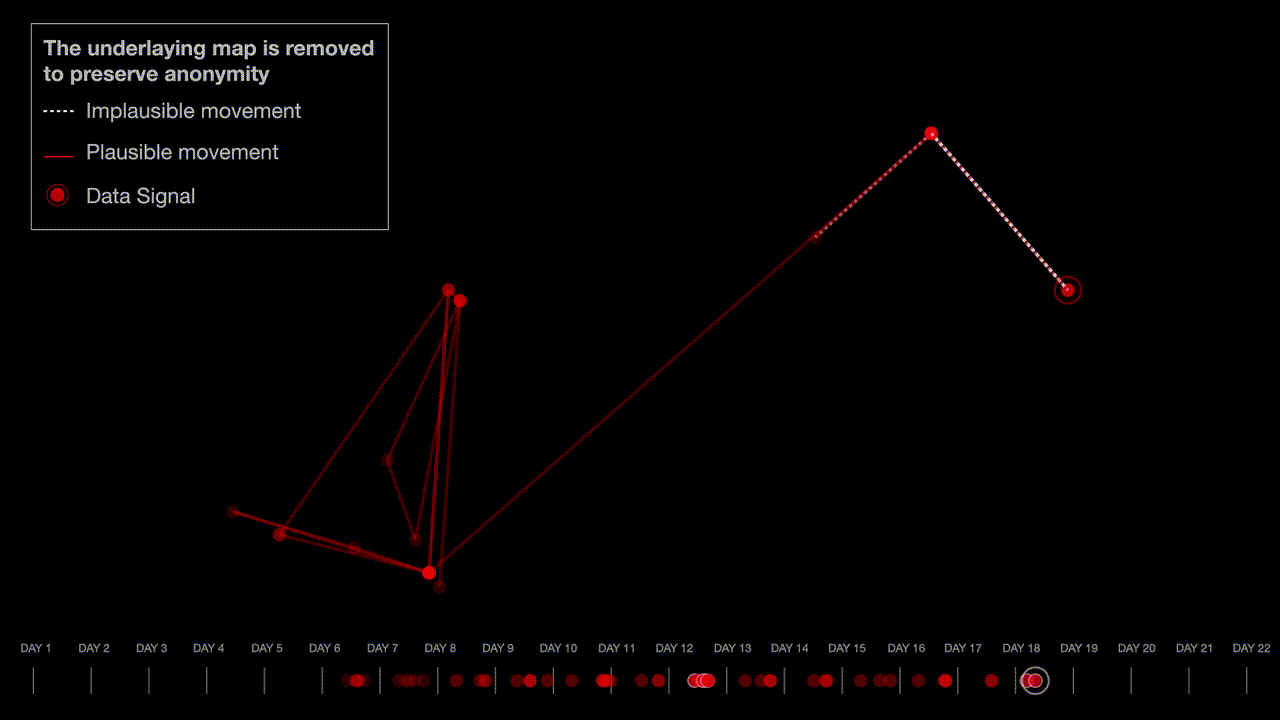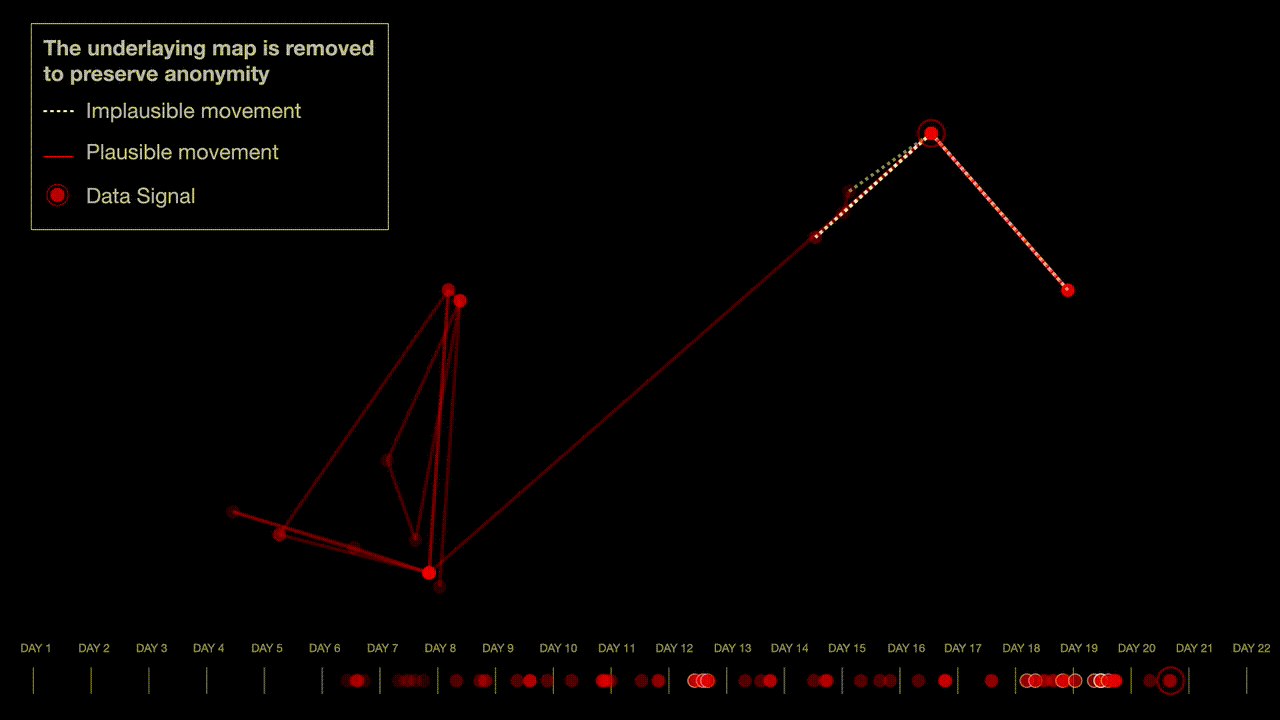
The researchers analyzed a sample of the exposed phone location data by looking for patterns they expected to see with real people’s location data, such as a concentration of people in major cities and by measuring the time it took for individuals to travel from one place to another. The researchers also found spatial irregularities that would be associated with real data, such as star-like patterns that are caused by a phone trying to accurately pinpoint its location when the line of sight to the satellite is obstructed by tall buildings.
“The spatial ‘irregularities’ in our sample — a common signature of real mobile location tracks — further support our assessment that this is real data. Therefore, the dataset is most likely not ‘dummy’ nor computer generated data, but rather reflects the movement of actual individuals, possibly acquired from telecommunications carriers or a third-party source,” the researchers said.
The researchers built maps, graphs, and visualizations to explain their findings, while preserving the anonymity of the individuals whose location data was fed into NSO’s Fleming demo.
Gary Miller, a mobile network security expert and founder of cyber intelligence firm Exigent Media, reviewed some of the datasets and graphs, and concluded it was real phone location data.
Miller said the number of data points increased around population hubs. “If you take a scatter plot of cell phone locations at a given point in time, there will be consistency in the number of points in suburban versus urban locations,” he said. Miller also found evidence of people traveling together, which he said “looked consistent with real phone data.”
He also said that even “anonymized” location data sets can be used to tell a lot about a person, such as where they live and work, and who they visit. “One can learn a lot of details about individuals simply by looking at location movement patterns,” he said.
“If you add up all of the similarities it would be very difficult to conclude that this was not actual mobile network data,” he said.
John Scott-Railton, a senior researcher at Citizen Lab, said the data likely originated from phone apps that use a blend of direct GPS data, nearby Wi-Fi networks, and the phone’s in-built sensors to try to improve the quality of the location data. “But it’s never really perfect,” he said. “If you’re looking at advertising data — like the kind that you buy from a data broker — it would look a lot like this.”
Scott-Railton also said that using simulated data for a contact-tracing system would be “counterproductive,” as NSO would “want to train [Fleming] on data that is as real and representative as possible.”
“Based on what I saw, the analysis provided by Forensic Architecture is consistent with the previous statements by Tehilla Shwartz Altshuler,” said Scott-Railton, referring to the academic who said NSO told her that was based on real data.
“The whole situation paints a picture of a spyware company once more being cavalier with sensitive and potentially personal information,” he said.
NSO rejected the researchers’ findings.
“We have not seen the supposed examination and have to question how these conclusions were reached. Nevertheless, we stand by our previous response of May 6, 2020. The demo material was not based on real and genuine data related to infected COVID-19 individuals,” said an unnamed spokesperson. (NSO’s earlier statement made no reference to individuals with COVID-19.)
“As our last statement details, the data used for the demonstrations did not contain any personally identifiable information (PII). And, also as previously stated, this demo was a simulation based on obfuscated data. The Fleming system is a tool that analyzes data provided by end users to help healthcare decision-makers during this global pandemic. NSO does not collect any data for the system, nor does NSO have any access to collected data.”
NSO did not answer our specific questions, including where the data came from and how it was obtained. The company claims on its website that Fleming is “already being operated by countries around the world,” but declined to confirm or deny its government customers when asked.
Contact Us
Got a tip? Contact us securely using SecureDrop. Find out more here.The Israeli spyware maker’s push into contact tracing has been seen as a way to repair its image, as the company battles a lawsuit in the United States that could see it reveal more about the governments that buy access to its Pegasus spyware.
NSO is currently embroiled in a lawsuit with Facebook-owned WhatsApp, which last year blamed NSO for exploiting an undisclosed vulnerability in WhatsApp to infect some 1,400 phones with Pegasus, including journalists and human rights defenders. NSO says it should be afforded legal immunity because it acts on behalf of governments. But Microsoft, Google, Cisco, and VMware filed an amicus brief this week in support of WhatsApp, and calling on the court to reject NSO’s claim to immunity.
The amicus brief came shortly after Citizen Lab found evidence that dozens of journalists were also targeted with Pegasus spyware by NSO customers, including Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. NSO disputed the findings.
A passwordless server run by spyware maker NSO sparks contact-tracing privacy concerns


























Comment