On the eve on the 2020 U.S. election, tensions are running high.
The good news? 2020 isn’t 2016. Social networks are way better prepared to handle a wide array of complex, dangerous or otherwise ambiguous Election Day scenarios.
The bad news: 2020 is its own beast, one that’s unleashed a nightmare health scenario on a divided nation that’s even more susceptible now to misinformation, hyper-partisanship and dangerous ideas moving from the fringe to the center than it was four years ago.
The U.S. was caught off guard by foreign interference in the 2016 election, but shocking a nation that’s spent the last eight months expecting a convergence of worst-case scenarios won’t be so easy.
Social platforms have braced for the 2020 election in a way they didn’t in 2016. Here’s what they’re worried about and the critical lessons from the last four years that they’ll bring to bear.
Contested election results
President Trump has repeatedly signaled that he won’t accept the results of the election in the case that he loses — a shocking threat that could imperil American democracy, but one social platforms have been tracking closely. Trump’s erratic, often rule-bending behavior on social networks in recent months has served as a kind of stress test, allowing those platforms to game out different scenarios for the election.
Facebook and Twitter in particular have laid out detailed plans about what happens if the results of the election aren’t immediately clear or if a candidate refuses to accept official results once they’re tallied.
On election night, Facebook will pin a message to the top of both Facebook and Instagram telling users that vote counting is still underway. When authoritative results are in, Facebook will change those messages to reflect the official results. Importantly, U.S. election results might not be clear on election night or for some days afterward, a potential outcome for which Facebook and other social networks are bracing.
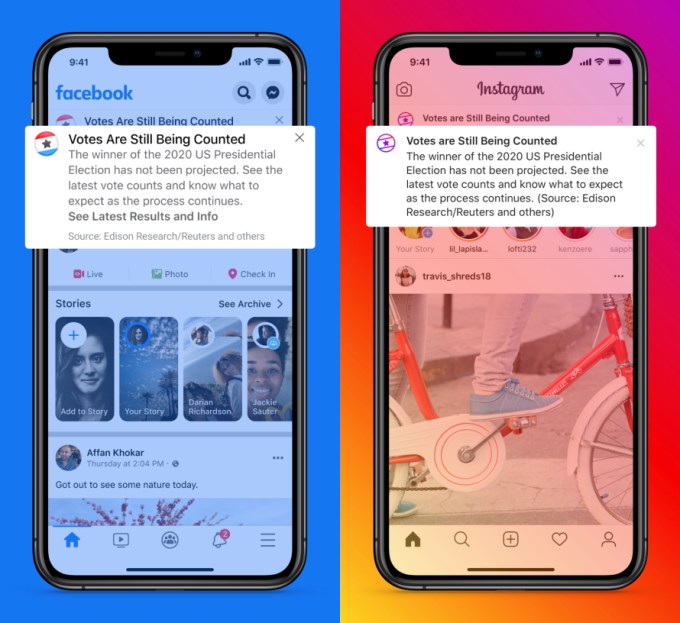
If a candidate declared victory prematurely, Facebook doesn’t say it will remove those claims, but it will pair them with its message that there’s no official result and voting is still underway.
Twitter released its plans for handling election results two months ago, explaining that it will either remove or attach a warning label to premature claims of victory before authoritative election results are in. The company also explicitly stated that it will act against any tweets “inciting unlawful conduct to prevent a peaceful transfer of power or orderly succession,” a shocking rule to have to articulate, but a necessary one in 2020.
On Monday, Twitter elaborated on its policy, saying that it would focus on labeling misleading tweets about the presidential election and other contested races. The company released a sample image of a label it would append, showing a warning stating that “this tweet is sharing inaccurate information.”
We may label Tweets, starting on election night, that make claims about election results before they’re officially called.
We’ll be prioritizing the presidential election and other highly contested races where there may be significant issues with misleading information. pic.twitter.com/BExhZdVMnB
— Support (@Support) November 2, 2020
Last week, the company also began showing users large misinformation warnings at the top of their feeds. The messages told users that they “might encounter misleading information” about mail-in voting and also cautioned them that election results may not be immediately known.
According to Twitter, users who try to share tweets with misleading election-related misinformation will see a pop-up pointing them to vetted information and forcing them to click through a warning before sharing. Twitter also says it will act on any “disputed claims” that might cast doubt on voting, including “unverified information about election rigging, ballot tampering, vote tallying, or certification of election results.”
One other major change that many users probably already noticed is Twitter’s decision to disable retweets. Users can still retweet by clicking through a pop-up page, but Twitter made the change to encourage people to quote retweet instead. The effort to slow down the spread of misinformation was striking, and Twitter said it will stay in place through the end of election week, at least.
YouTube didn’t go into similar detail about its decision making, but the company previously said it will put an “informational” label on search results related to the election and below election-related videos. The label warns users that “results may not be final” and points them to the company’s election info hub.
YouTube will add vetted info about mail-in voting to counter election misinformation
Foreign disinformation
This is one area where social networks have made big strides. After Russian disinformation took root on social platforms four years ago, those companies now coordinate with one another and the government about the threats they’re seeing.
In the aftermath of 2016, Facebook eventually woke up to the idea that its platform could be leveraged to scale social ills like hate and misinformation. Its scorecard is uneven, but its actions against foreign disinformation have been robust, reducing that threat considerably.
A repeat of the same concerns from 2016 is unlikely. Facebook made aggressive efforts to find foreign coordinated disinformation campaigns across its platforms, and it publishes what it finds regularly and with little delay. But in 2020, the biggest concerns are coming from within the country — not without.
Most foreign information operations have been small so far, failing to gain much traction. Last month, Facebook removed a network of fake accounts connected to Iran. The operation was small and failed to generate much traction, but it shows that U.S. adversaries are still interested in trying out the tactic.
Misleading political ads
To address concerns around election misinformation in ads, Facebook opted for a temporary political ad blackout, starting at 12 a.m. PT on November 4 and continuing until the company deems it safe to toggle them back on. Facebook hasn’t accepted any new political ads since October 27 and previously said it won’t accept any ads that delegitimize the results of the election. Google will also pause election-related ads after polls close Tuesday.
Facebook has made a number of big changes to political ads since 2016, when Russia bought Facebook ads to meddle with U.S. politics. Political ads on the platform are subject to more scrutiny and much more transparency now and Facebook’s ad library emerged as an exemplary tool that allows anyone to see what ads have been published, who bought them and how much they spent.
Unlike Facebook, Twitter’s way of dealing with political advertising was cutting it off entirely. The company announced the change a year ago and hasn’t looked back since. TikTok also opted to disallow political ads.
We’ve made the decision to stop all political advertising on Twitter globally. We believe political message reach should be earned, not bought. Why? A few reasons…🧵
— jack (@jack) October 30, 2019
Political violence
Politically motivated violence is a big worry this week in the U.S. — a concern that shows just how tense the situation has grown under four years of Trump. Leading into Tuesday, the president has repeatedly made false claims of voter fraud and encouraged his followers to engage in voter intimidation, a threat Facebook was clued into enough that it made a policy prohibiting “militarized” language around poll watching.
Facebook: Trump can’t recruit ‘army’ of poll watchers under new voter intimidation rules
Facebook made a number of other meaningful recent changes, like banning the dangerous pro-Trump conspiracy theory QAnon and militias that use the platform to organize, though those efforts have come very late in the game.
Facebook was widely criticized for its inaction around a Trump post warning “when the looting starts, the shooting starts” during racial justice protests earlier this year, but its recent posture suggests similar posts might be taken more seriously now. We’ll be watching how Facebook handles emerging threats of violence this week.
Its recent decisive moves against extremism are important, but the platform has long incubated groups that use the company’s networking and event tools to come together for potential real-world violence. Even if they aren’t allowed on the platform any longer, many of those groups got organized and then moved their networks onto alternative social networks and private channels. Still, making it more difficult to organize violence on mainstream social networks is a big step in the right direction.
Twitter also addressed the potential threat of election-related violence in advance, noting that it may add warnings or require users to remove any tweets “inciting interference with the election” or encouraging violence.
Platform policy shifts in 2020
Facebook is the biggest online arena where U.S. political life plays out. While a similar number of Americans watch videos on YouTube, Facebook is where they go to duke it out over candidates, share news stories (some legitimate, some not) and generally express themselves politically. It’s a tinderbox in normal times — and 2020 is far from normal.
While Facebook acted against foreign threats quickly after 2016, the company dragged its feet on platform changes that could be perceived as politically motivated — a hesitation that backfired by incubating dangerous extremists and allowing many kinds of misinformation, particularly on the far-right, to survive and thrive.
In spite of Facebook’s lingering misguided political fears, there are reasons to be hopeful that the company might avert election-related catastrophes.
Whether it was inspired by the threat of a contested election, federal antitrust action or a possible Biden presidency, Facebook has signaled a shift to more thoughtful moderation with a flurry of recent policy enforcement decisions. An accompanying flurry of election-focused podcast and television ads suggests Facebook is worried about public perception too — and it should be.
Twitter’s plan for the election has been well-communicated and detailed. In 2020, the company treats its policy decisions with more transparency, communicates them in real time and isn’t afraid to admit to mistakes. The relatively small social network plays an outsized role in publishing political content that’s amplified elsewhere, so the choices it makes are critical for countering misinformation and extremism.
The companies that host and amplify online political conversation have learned some major lessons since 2016 — mostly the hard way. Let’s just hope it was enough to help them guide their roiling platforms through one of the most fraught moments in modern U.S. history.































Comment