Alice Lloyd George
More posts from Alice Lloyd George
It’s hard to visit a tech site these days without seeing a headline about deep learning for X, and that AI is on the verge of solving all our problems. Gary Marcus remains skeptical.
Marcus, a best-selling author, entrepreneur and professor of psychology at NYU, has spent decades studying how children learn, and believes that throwing more data at problems won’t necessarily lead to progress in areas such as understanding language, not to speak of getting us to AGI — artificial general intelligence.
Marcus is the voice of anti-hype at a time when AI is all the hype, and in 2015 he translated his thinking into a startup, Geometric Intelligence, which uses insights from cognitive psychology to build better-performing, less-data-hungry machine learning systems. The team was acquired by Uber in December to run Uber’s AI labs, where his co-founder Zoubin Ghahramani has now been appointed chief scientist. So what did the tech giant see that was so important?
In an interview for Flux, I sat down with Marcus, who discussed why deep learning is the hammer that’s making all problems look like a nail and why his alternative sparse data approach is so valuable.
We also got into the challenges of being an AI startup competing with the resources of Google, how corporates aren’t focused on what society actually needs from AI, his proposal to revamp the outdated Turing test with a multi-disciplinary AI triathlon and why programming a robot to understand “harm” is so difficult.
AMLG: Gary, you are well-known as a critic of this technique, you’ve said that it’s over-hyped. That there’s low-hanging fruit that deep learning’s good at — specific narrow tasks like perception and categorization, and maybe beating humans at chess, but you felt that this deep learning mania was taking the field of AI in the wrong direction, that we’re not making progress on cognition and strong AI. Or as you’ve put it, “we wanted Rosie the robot, and instead we got the Roomba.” So you’ve advocated for bringing psychology back into the mix, because there’s a lot of things that humans do better, and that we should be studying humans to understand why they do things better. Is this still how you feel about the field?
GM: Pretty much. There was probably a little more low-hanging fruit than I anticipated. I saw somebody else say it more concisely, which is simply, deep learning does not equal AGI (AGI is “artificial general intelligence.”) There’s all the stuff you can do with deep learning, like it makes your speech recognition better. It makes your object recognition better. But that doesn’t mean it’s intelligence. Intelligence is a multi-dimensional variable. There are lots of things that go into it.
In a talk I gave at TEDxCERN recently, I made this kind of pie chart and I said look, here’s perception, that’s a tiny slice of the pie. It’s an important slice of the pie, but there’s lots of other things that go into human intelligence, like our ability to attend to the right things at the same time, to reason about them to build models of what’s going on in order to anticipate what might happen next and so forth. And perception is just a piece of it. And deep learning is really just helping with that piece.
In a New Yorker article that I wrote in 2012, I said look, this is great, but it’s not really helping us solve causal understanding. It’s not really helping with language. Just because you’ve built a better ladder doesn’t mean you’ve gotten to the moon. I still feel that way. I still feel like we’re actually no closer to the moon, where the moonshot is intelligence that’s really as flexible as human beings. We’re no closer to that moonshot than we were four years ago. There’s all this excitement about AI, and it’s well deserved. AI is a practical tool for the first time and that’s great. There’s good reason for companies to put in all of this money. But just look for example at a driverless car, that’s a form of intelligence, modest intelligence, the average 16-year-old can do it as long as they’re sober, with a couple of months of training. Yet Google has worked on it for seven years and their car still can only drive — as far as I can tell, since they don’t publish the data — like on sunny days, without too much traffic…
AMLG: And isn’t there the whole black box problem that you don’t know what’s going on. We don’t know the inner workings of deep learning, it’s kind of inscrutable. Isn’t that a massive problem for things like driverless cars?
GM: It is a problem. Whether it’s an insuperable problem is an open empirical question. So it is a fact at least for now that we can’t well interpret what deep learning is doing. So the way to think about it is you have millions of parameters and millions of data points. That means that if I as an engineer look at this thing I have to contend with these millions or billions of numbers that have been set based on all of that data and maybe there is a kind of rhyme or reason to it but it’s not obvious and there’s some good theoretical arguments to think sometimes you’re never really going to find an interpretable answer there.
There’s an argument now in the literature which goes back to some work that I was doing in the 90s about whether deep learning is just memorization. So this was the paper that came out that said it is and another says no it isn’t. Well it isn’t literally exactly memorization but it’s a little bit like that. If you memorize all these examples, there may not be some abstract rule that characterizes all of what’s going on but it might be hard to say what’s there. So if you build your system entirely with deep learning, which is something that Nvidia has played around with, and something goes wrong, it’s hard to know what’s going on and that makes it hard to debug.
AMLG: Which is a problem if your car just runs into a lamppost and you can’t debug why that happened.
GM: You’re lucky if it’s only a lamppost and not too many people are injured. There are serious risks here. Somebody did die, though I think it wasn’t a deep learning system in the Tesla crash, it was a different kind of system. We actually have problems on engineering on both ends. So I don’t want to say that classical AI has fully licked these problems, it hasn’t. I think it’s been abandoned prematurely and people should come back to it. But the fact is we don’t have good ways of engineering really complex systems. And minds are really complex systems.
AMLG: Why do you think these big platforms are reorganizing around AI and specifically deep learning? Is it just that they’ve got data moats, so you might as well train on all of that data if you’ve got it?
GM: Well there’s an interesting thing about Google, which is they have enormous amounts of data. So of course they want to leverage it. Google has the power to build new resources that they give away free and they build the resources that are particular to their problem. So Google, because they have this massive amount of data, has oriented their AI around, how can I leverage that data? Which makes sense from their commercial interests. But it doesn’t necessarily mean, say from a society’s perspective, does society need AI? What does it need it for? Would it be the best way to build it?

CERN is a vast interdisciplinary, multi-country consortium to solve particular scientific problems, maybe we need the same thing for AI. Most of the efforts in AI right now are individual companies or small labs working on small problems like how to sell more advertising… what if we brought people together to try this moonshot of doing better science, and what if we brought not just machine learning experts, and engineers who can make faster hardware, but researchers who look at cognitive development. I think we could make some progress. Gary Marcus
I think if you asked those questions you would say, well what society most needs is automated scientific discovery that can help us actually understand the brain to cure neural disorders, to actually understand cancer to cure cancer, and so forth. If that were the thing we were most trying to solve in AI, I think we would say, let’s not leave it all in the hands of these companies. Let’s have an international consortium kind of like we had for CERN, the large hadron collider. That’s seven billion dollars. What if you had $7 billion dollars that was carefully orchestrated towards a common goal. You could imagine society taking that approach. It’s not going to happen right now given the current political climate.
AMLG: Well they are sort of at least coming together on AI ethics. So that’s a start.
GM: It is good that people are talking about the ethical issues and there are serious issues that deserve consideration. The only thing I would say there is, some people are hysterical about it, thinking that real AI is around the corner and it probably isn’t. I think it’s still OK that we start thinking about these things now, even if real AI is further away than people think it is. If that’s what moves people into action and it takes 20 years, but the action itself takes 20 years, then it’s the right timing to start thinking about it now.
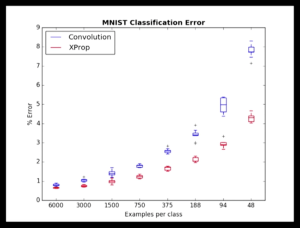
AMLG: I want to get back to your alternative approach to solving AI, and why it’s so important. So you’ve come up with what you believe is a better paradigm, taking inspiration from cognitive psychology. The idea is that your algorithms are a much quicker study, that they’re more efficient and less data hungry, less brittle and that they can have broader applicability. And in a brief amount of time you’ve had impressive early results. You’ve run a bunch of image recognition tests comparing the techniques and have shown that your algorithms perform better, using smaller amounts of data, often called sparse data. So deep learning works well when you have tons of data for common examples and high-frequency things. But in the real world, in most domains, there’s a long tail of things where there isn’t a lot of data. So while neural nets may be good at low-level perception, they aren’t as good at understanding integrated wholes. So tell us more about your approach, and how your training in cognitive neuroscience has informed it.
GM: My training was with Steve Pinker. And through that training I became sensitive to the fact that human children are very good at learning language, phenomenally good, even when they’re not that good at other things. Of course I read about that as a graduate student, now I have some human children, I have a four-year-old and a two-and-a-half year old. And it’s just amazing how fast they learn.
AMLG: The best AIs you’ve ever seen?
GM: The best AIs I’ve ever seen. Actually, my son shares a birthday with Rodney Brooks, who’s one of the great roboticists, I think you know him well. For a while I was sending Rodney an e-mail message every year saying “Happy birthday. My son is now a year old. I think he can do this and your robots can’t.” It was kind of a running joke between us.
AMLG: And now he’s vastly superior to all of the robots.
GM: And I didn’t even bother this year. The four-year-olds of this world, what they can do in terms of motor control and language is far ahead of what robots can do. And so I started thinking about that kind of question really in the early 90s. And I’ve never fully figured out the answer, but part of the motivation for my company was, hey we have these systems now that are pretty good at learning if you have gigabytes of data, and that’s great work if you can get it, and you can get it sometimes. So speech recognition, if you’re talking about white males asking search queries in a quiet room, you can get as much labelled data, which is critical, for these systems as you want. This is how somebody says something and this is the word written out. But my kids don’t need that. They don’t have labelled data, they don’t have gigabytes of label data they just kind of watch the world and they figure all this stuff out.































Comment