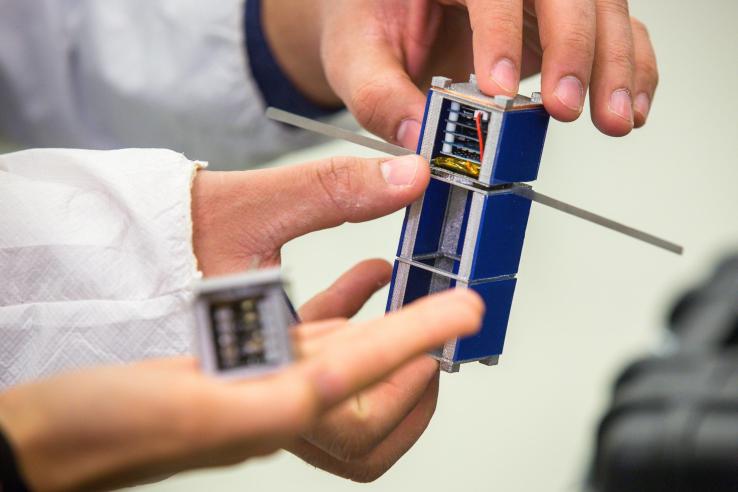
The future is small in space: picture Cubesats the size of toasters and Femtosats an inch across crowding the skies. A newly invented motor that’s both tiny and powerful goes hand in hand with that vision, providing compact spacecraft with the ability to adjust their position without using a drop of fuel.
First, though, a little engineering lesson. Here comes the science!
It’s not practical, especially in small, long-mission spacefaring units like satellites and probes, to use fuel for much of anything except critical accelerations and maneuvers. After all, you can’t exactly top off a New Horizons when it runs low on hydrazine. So in order to make small adjustments to a craft’s attitude, reaction wheels are often employed.
Basically, these things are flywheels mounted inside the satellite that spin at a constant speed — and varying that speed (say by slowing counterclockwise spin on the Y axis), results in a reactive force from the satellite. Every action has its reaction, remember? And in this case, the reaction is that the satellite rotates around its center of mass proportionally to how much the wheel’s speed is altered.
Like most things that rotate really fast, reaction wheels use ball bearings. But these bearings wear down over time and must be sealed carefully against vacuum and other things that might damage them. The Hubble has had two wheels replaced, and Kepler has lost functionality because of blown wheel mechanisms. Not only that, but even under nominal operation, the slight imperfections in every bearing add up, creating vibrations that can interfere with scientific instruments.
This will be on the quiz.
Arda Tüysüz at Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule Zürich (we’ll go with ETH for now) and his colleagues at Celeroton, a company spun off from the school, thought there must be a better way. And so there was! In fact, the solution was so simple one wonders why we didn’t do it years ago: use magnets instead of bearings.
“There is nothing particularly new about it. The electronics, the magnetic bearings, understanding of the basic physical principle — it was all there already,” Tüysüz said in an ETH Zurich news release.
By magnetically levitating the wheel, all kinds of problems are avoided and new possibilities unlocked. For one thing, losing the bearings means there’s no need for a vacuum-sealed chamber, lubrication or anything like that. There’s no vibration, nothing to replace. And because friction and mechanical wear are trivial in a free-floating rotor, it can be spun faster than a traditional reaction wheel — a lot faster.
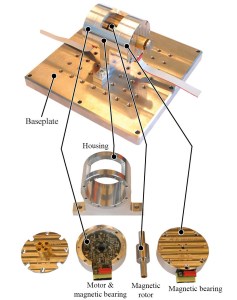
While mechanically operated wheels generally spin at a few thousand RPM, this floating one can be dialed all the way up to an incredible 150,000 RPM. This means 10- or 20-fold increased power from a motor the same size as a mechanical one — but perhaps more importantly, it means you can get the same power levels as before from a motor a tenth the size.
For small spacecraft this could be a revelation: compact, efficient and powerful rotational motors that never wear out. Freeing up even a few cubic inches is a huge boon for just about any mission — that’s space that could be used for another instrument, a battery or fuel, or left empty to reduce launch mass.
It’s no surprise that the European Space Agency has expressed interest in the system, even though at present the motor is still in prototype phase.
Tüysüz and his colleagues from ETH Zurich and Celeroton published the details of their creation in a paper presented at a conference in Capri.






























Comment