John Rampton
More posts from John Rampton
By now everyone has heard of Google’s RankBrain, the new artificial intelligence machine learning algorithm that is supposed to be the latest and greatest from Mountain View, Calif. What many of you might not realize, however, is just how fast the SEO industry is changing because of it. In this article, I’ll take you through some clear examples of how some of the old rules of SEO no longer apply, and what steps you can take to stay ahead of the curve in order to continue to provide successful SEO campaigns for your businesses.
So what is artificial intelligence?
There are generally three different classifications of artificial intelligence:
- Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI): This is like AI for one particular thing (e.g. beating the world champion in chess).
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): This is when the AI can perform all things. Once an AI can perform like a human, we consider it AGI.
- Artificial Superintelligence (ASI): AI on a much higher level for all things (e.g. beyond the capabilities of a single human).
When we talk about the context of Google’s RankBrain, and the machine learning algorithms that are currently running on Google, we are talking about Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI).
Actually, ANI has been around for some time. Ever wonder how those SPAM filters work in your email? Yep, that’s ANI. Here are some of my favorite ANI programs: Google Translate, IBM’s Watson, that cool feature on Amazon that tells you products that are “recommended for you,” self-driving cars and, yes, our beloved Google’s RankBrain.
Within ANI, there are many different approaches. As Pedro Domingos clearly lays out in his book The Master Algorithm, data scientists trying to achieve the perfect AI can be grouped into five “tribes” today:
- Symbolists
- Connectionists
- Evolutionaries
- Bayesians
- Analogizers
Google’s RankBrain is in the camp of the Connectionists. Connectionists believe that all our knowledge is encoded in the connections between neurons in our brain. And RankBrain’s particular strategy is what experts in the field call a back propagation technique, rebranded as “deep learning.”
Connectionists claim this strategy is capable of learning anything from raw data, and therefore is also capable of ultimately automating all knowledge discovery. Google apparently believes this, too. On January 26th, 2014, Google announced it had agreed to acquire DeepMind Technologies, which was, essentially, a back propagation shop.
So when we talk about RankBrain, we now can tell people it is comprised of one particular technique (back propagation or “deep learning”) on ANI. Now that we have that out of the way, just how much is this field progressing? And, more importantly, how is it changing the business of SEO?
The exponential growth of technology (and AI)
Tim Urban from WaitButWhy.com explains the growth of technology better than anyone in his article The AI Revolution: The Road to Superintelligence.
Here is what technological progress looks like, when you look back at history:
But, as Urban points out, in reality, you can’t see what’s to your right (the future). So here is how it actually feels when you are standing there:
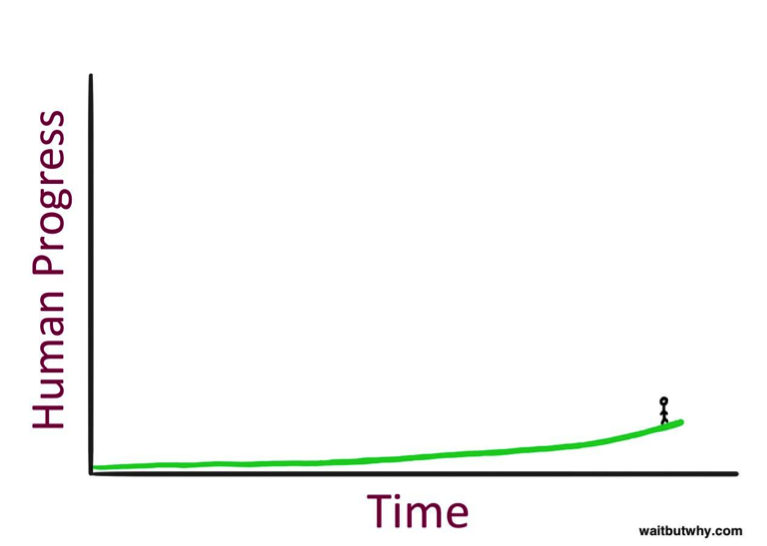
What this chart shows is that when humans try to predict the future, they always underestimate. This is because they are looking to the left of this graph, instead of to the right.
However, the reality is, human progress takes place at a faster and faster rate as time goes on. Ray Kurzweil calls this the Law of Accelerating Returns. The scientific reasoning behind his original theory is that more advanced societies have the ability to progress at a faster rate than less advanced societies — because they’re more advanced. Of course, the same can be applied to artificial intelligence and the growth rate we are seeing now with advanced technology.
We see this with computing resources right now. Here is a visualization that gives you the perspective of just how fast things can change because of this Law of Accelerating Returns:
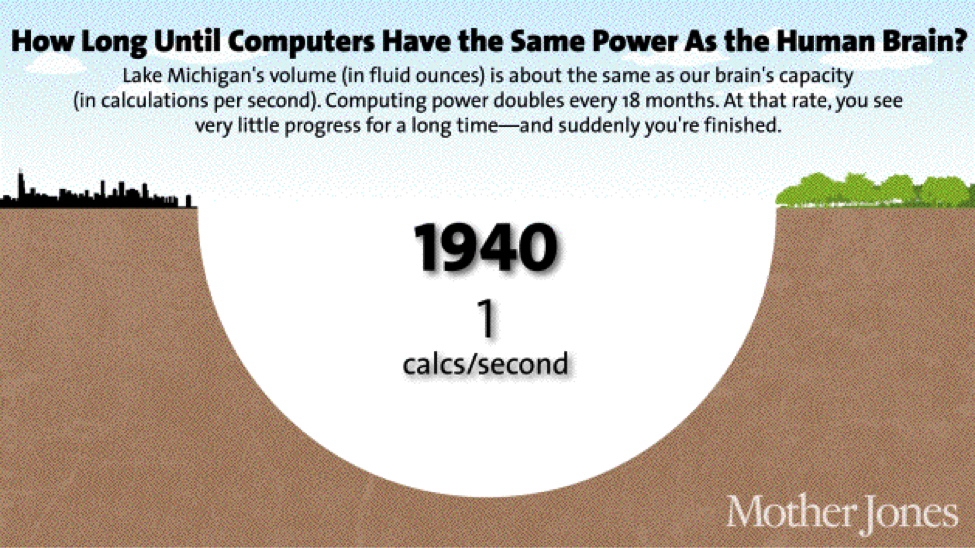
As you can clearly see, and as we all can intuitively feel, the growth of advanced processing and computers has benefited from this Law of Accelerating Returns. Here is another shocking revelation: At some point, the processing power for an economical computer will surpass that of not only a single human, but for all humans combined.
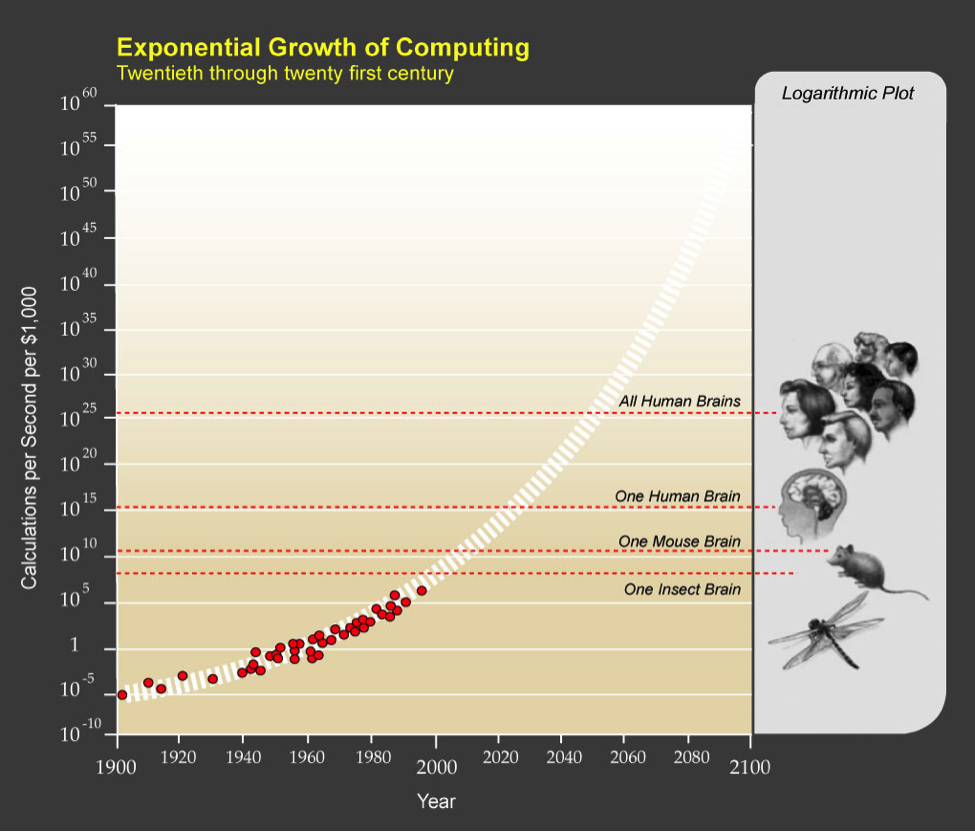
In fact, it now appears that we will be able to achieve Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) some time around 2025. Technology is clearly expanding at a faster and faster pace, and, by many accounts, most of us will be caught off guard.
The rise of superintelligence
As I have explained above, Google’s RankBrain is just one form of ANI, which means that, while it can perform things better than a human in one specific area, it is just that: a relatively weak form of artificial intelligence.
But we may be blindsided by how fast this “weak” intelligence might easily turn into something with which we have no idea how to deal.
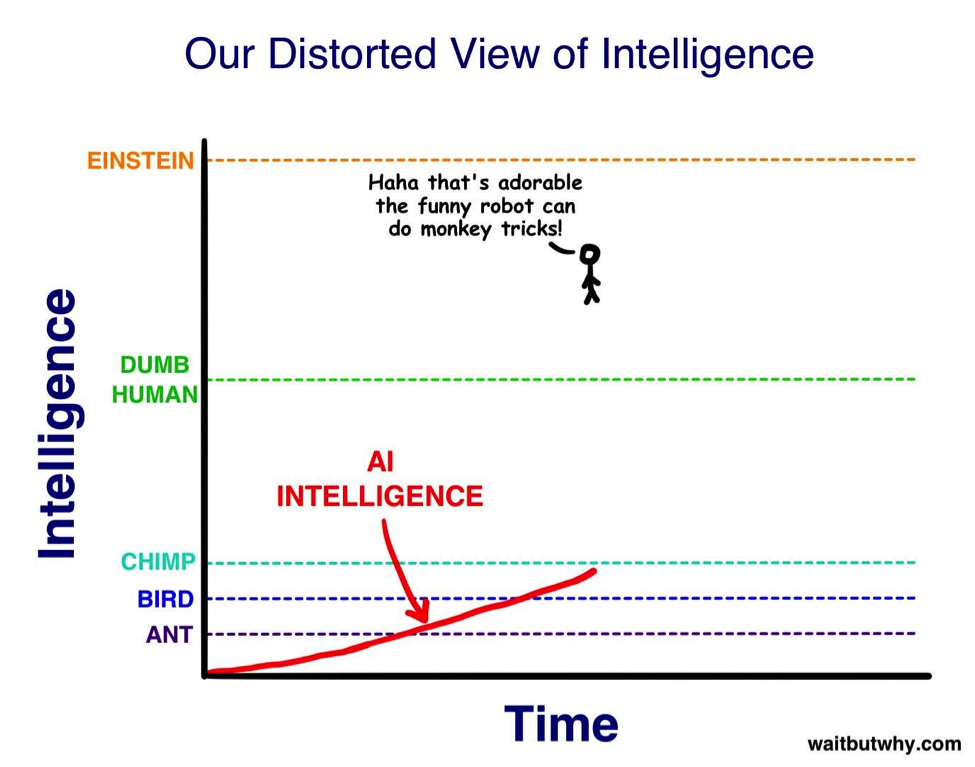
Here, you can clearly see that Google’s RankBrain, while super intelligent on one particular task, is still in the general context of things, fairly unintelligent on the intelligence scale.
But what happens when we apply the same Law of Accelerating Returns to artificial intelligence? Tim Urban walks us through the thought experiment:
“…so as A.I. zooms upward in intelligence toward us, we’ll see it as simply becoming smarter, for an animal. Then, when it hits the lowest capacity of humanity — Nick Bostrom uses the term ‘the village idiot’ — we’ll be like, ‘Oh wow, it’s like a dumb human. Cute!’ The only thing is, in the grand spectrum of intelligence, all humans, from the village idiot to Einstein, are within a very small range — so just after hitting village idiot level and being declared to be AGI, it’ll suddenly be smarter than Einstein and we won’t know what hit us.”
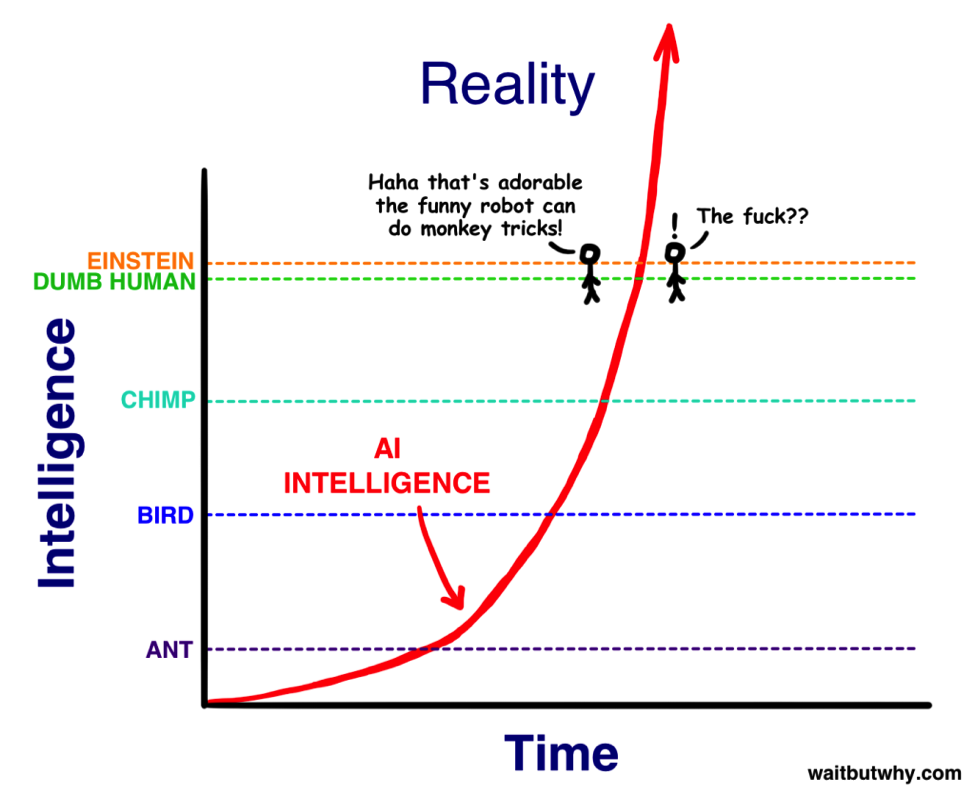
So what does this mean for the business of SEO and the artificial intelligence that is upon us?
SEO has changed forever
Before we get into predicting the future, let’s take inventory on how RankBrain has already changed SEO. I sat down with Carnegie Mellon alumnus and friend Scott Stouffer, now CTO and co-founder of Market Brew, a company that provides search engine models for Fortune 500 SEO teams. As a search engineer himself, Stouffer had a unique perspective over the past decade that most professionals in that industry don’t get to see. Here are some of his tips for the SEO industry when it comes to Google’s new emphasis on artificial intelligence.
Today’s regression analysis is seriously flawed
This is the biggest current fallacy of our industry. There have been many prognosticators every time Google’s rankings shift in a big way. Usually, without fail, a few data scientists and CTOs from well-known companies in our industry will claim they “have a reason!” for the latest Google Dance. The typical analysis consists of perusing through months of ranking data leading up to the event, then seeing how the rankings shifted across all websites of different types.
With today’s approach to regression analysis, these data scientists point to a specific type of website that has been affected (positively or negatively) and conclude with high certainty that Google’s latest algorithmic shift was attributed to a specific type of algorithm (content or backlink, et al.) that these websites shared.
However, that isn’t how Google works anymore. Google’s RankBrain, a machine learning or deep learning approach, works very differently.
Within Google, there are a number of core algorithms that exist. It is RankBrain’s job to learn what mixture of these core algorithms is best applied to each type of search results. For instance, in certain search results, RankBrain might learn that the most important signal is the META Title.
Adding more significance to the META Title matching algorithm might lead to a better searcher experience. But in another search result, this very same signal might have a horrible correlation with a good searcher experience. So in that other vertical, another algorithm, maybe PageRank, might be promoted more.
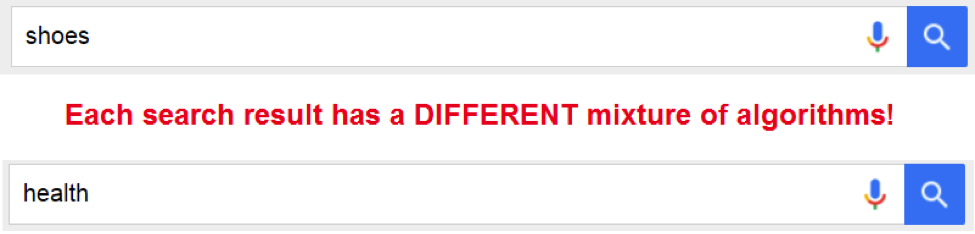
This means that, in each search result, Google has a completely different mix of algorithms. You can now see why doing regression analysis over every site, without having the context of the search result that it is in, is supremely flawed.
For these reasons, today’s regression analysis must be done by each specific search result. Stouffer recently wrote about a search modeling approach where the Google algorithmic shifts can be measured. First, you can take a snapshot of what the search engine model was calibrated to in the past for a specific keyword search. Then, re-calibrate it after a shift in rankings has been detected, revealing the delta between the two search engine model settings. Using this approach, during certain ranking shifts, you can see which particular algorithm is being promoted or demoted in its weighting.
Having this knowledge, we can then focus on improving that particular part of SEO for sites for those unique search results. But that same approach will not (and cannot) hold for other search results. This is because RankBrain is operating on the search result (or keyword) level. It is literally customizing the algorithms for each search result.
Stay niche to avoid misclassification
What Google also realized is that they could teach their new deep learning system, RankBrain, what “good” sites look like, and what “bad” sites look like. Similar to how they weight algorithms differently for each search result, they also realized that each vertical had different examples of “good” and “bad” sites. This is undoubtedly because different verticals have different CRMs, different templates and different structures of data altogether.
When RankBrain operates, it is essentially learning what the correct “settings” are for each environment. As you might have guessed by now, these settings are completely dependent on the vertical on which it is operating. So, for instance, in the health industry, Google knows that a site like WebMD.com is a reputable site that they would like to have near the top of their searchable index. Anything that looks like the structure of WebMD’s site will be associated with the “good” camp. Similarly, any site that looks like the structure of a known spammy site in the health vertical will be associated with the “bad” camp.
As RankBrain works to group “good” and “bad” sites together, using its deep learning capabilities, what happens if you have a site that has many different industries all rolled up into one?
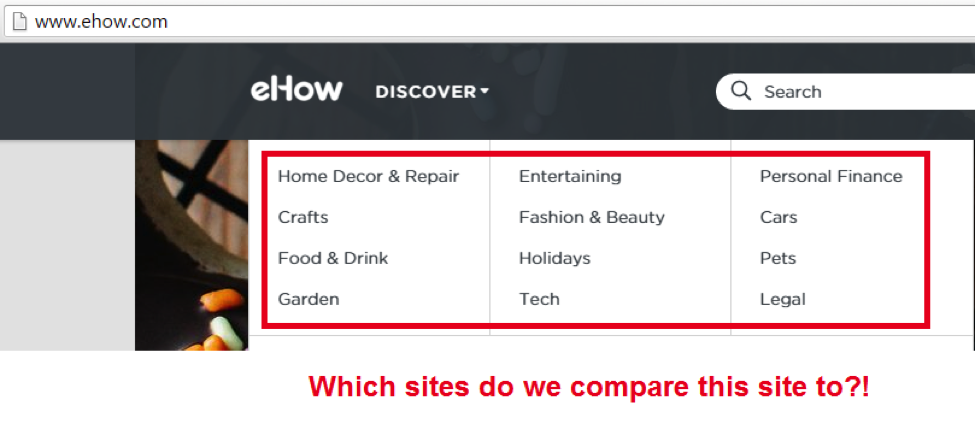
First, we have to discuss a bit more detail on how exactly this deep learning works. Before grouping together sites into a “good” and “bad” bucket, RankBrain must first determine what each site’s classification is. Sites like Nike.com and WebMD.com are pretty easy. While there are many different sub-categories on each site, the general category is very straightforward. These types of sites are easily classifiable.
But what about sites that have many different categories? A good example of these types of sites are the How-To sites. Sites that typically have many broad categories of information. In these instances, the deep learning process breaks down. Which training data does Google use on these sites? The answer is: It can be seemingly random. It may choose one category or another. For well-known sites, like Wikipedia, Google can opt-out of this classification process altogether, to ensure that the deep learning process doesn’t undercut their existing search experience (aka “too big to fail”).
But for lesser-known entities, what will happen? The answer is, “Who knows?” Presumably, this machine learning process has an automated way of classifying each site before attempting to compare it to other sites. Let’s say a How-To site looks just like WebMD’s site. Great, right?
Well, if the classification process thinks this site is about shoes, then it is going to be comparing the site to Nike’s site structure, not WebMD’s. It just might turn out that their site structure looks a lot like a spammy shoe site, as opposed to a reputable WebMD site, in which case the overly generalized site could easily be flagged as SPAM. If the How-To site had separate domains, then it would be easy to make each genre look like the best of that industry. Stay niche.
These backlinks smell fishy
Let’s take a look at how this affects backlinks. Based on the classification procedure above, it is more important than ever to stick within your “linking neighborhood,” as RankBrain will know if something is different from similar backlink profiles in your vertical.
Let’s take the same example as above. Say a company has a site about shoes. We know that RankBrain’s deep learning process will attempt to compare each aspect of this site with the best and worst sites of the shoe industry. So, naturally, the backlink profile of this site will be compared to the backlink profiles of these best and worst sites.
Let’s also say that a typical reputable shoe site has backlinks from the following neighborhoods:
- Sports
- Health
- Fashion
Now let’s say that the company’s SEO team decides to start pursuing backlinks from all these neighborhoods, plus a new neighborhood — from one of the CEO’s previous connections to the auto industry. They are “smart” about it as well: They construct a cross-marketing “free shoe offer for all new leases” page that is created on the auto site, which then links to their new type of shoe. Totally relevant, right?
Well, RankBrain is going to see this and notice that this backlink profile looks a lot different than the typical reputable shoe site. Worse yet, it finds that a bunch of spammy shoe sites also have a backlink profile from auto sites. Uh oh.
And just like that, without even knowing what is the “correct” backlink profile, RankBrain has sniffed out what is “good” and what is “bad” for its search engine results. The new shoe site is flagged, and their organic traffic takes a nosedive.
The future of SEO and artificial intelligence
As we can see from the previous discussion on the Law of Accelerating Returns, RankBrain and other forms of artificial intelligence will at some point surpass the human brain. And at this point, nobody knows where this technology will lead us.
Some things are certain, though:
- Each competitive keyword environment will need to be examined on its own;
- Most sites will need to stay niche to avoid misclassification; and
- Each site should mimic the structure and composition of their respective top sites in that niche.
In some ways, the deep learning methodology makes things simpler for SEOs. Knowing that RankBrain and similar technologies are almost on par with a human, the rule of law is clear: There are no more loopholes.
In other ways, things are a bit harder. The field of SEO will continue to become extremely technical. Analytics and big data are the order of the day, and any SEO that isn’t familiar with these approaches has a lot of catching up to do. Those of you who have these skills can look forward to a big payday.






























Comment