In a mind-boggling world first, a team of biologists and security researchers have successfully infected a computer with a malicious program coded into a strand of DNA.
It sounds like science fiction, but I assure you it’s quite real — although you probably don’t have to worry about this particular threat vector any time soon. That said, the possibilities suggested by this project are equally fascinating and terrifying to contemplate.
The multidisciplinary team at the University of Washington isn’t out to make outlandish headlines, although it’s certainly done that. They were concerned that the security infrastructure around DNA transcription and analysis was inadequate, having found elementary vulnerabilities in open-source software used in labs around the world. Given the nature of the data usually being handled, this could be a serious problem going forward.
Sure, they could demonstrate the weakness of the systems with the usual malware and remote access tools. That’s how any competent attacker would come at such a system. But the discriminating security professional prefers to stay ahead of the game.
“One of the big things we try to do in the computer security community is to avoid a situation where we say, ‘Oh shoot, adversaries are here and knocking on our door and we’re not prepared,’” said professor Tadayoshi Kohno, who has a history of pursuing unusual attack vectors for embedded and niche electronics like pacemakers.
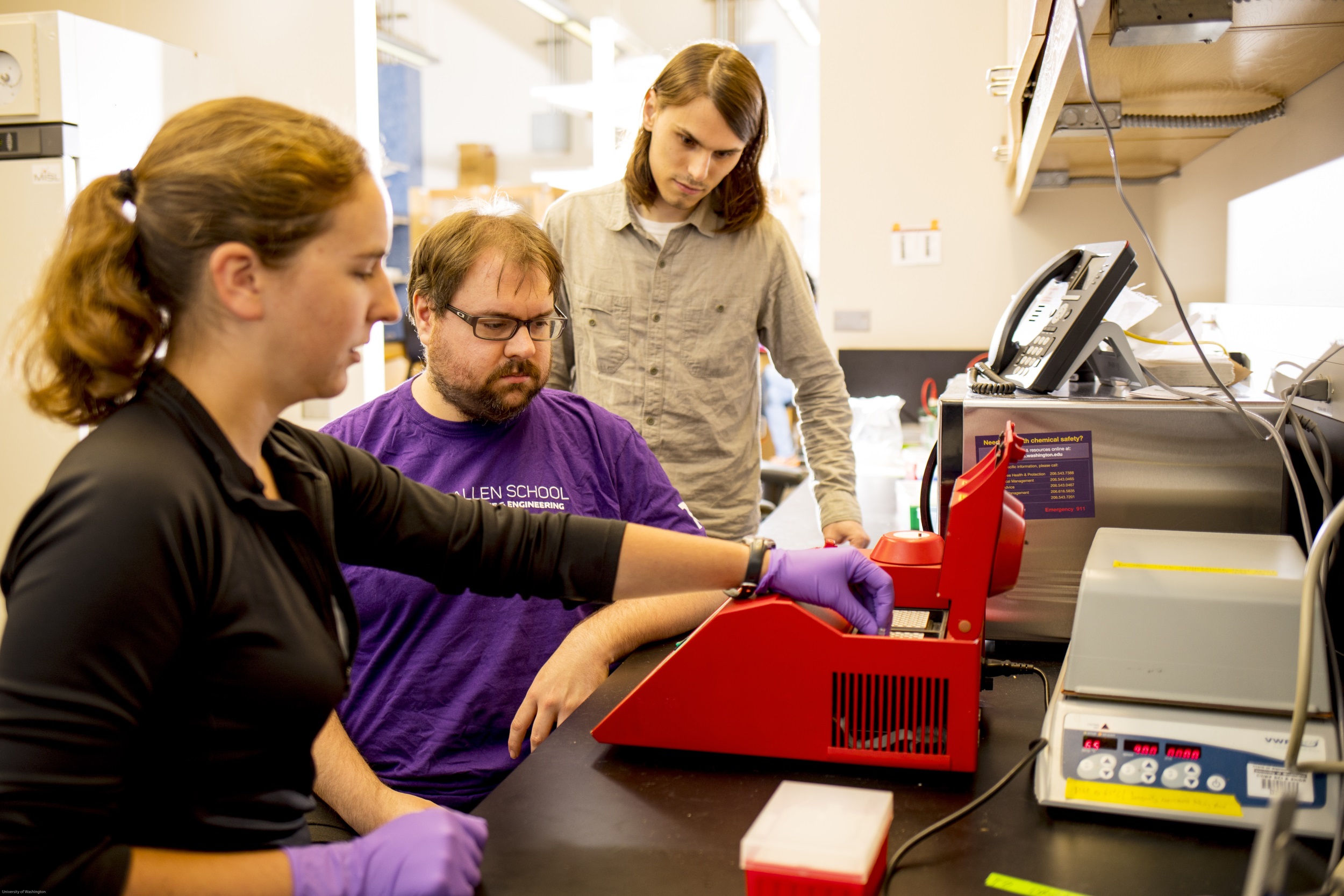

“As these molecular and electronic worlds get closer together, there are potential interactions that we haven’t really had to contemplate before,” added Luis Ceze, one co-author of the study.
Accordingly, they made the leap plenty of sci-fi writers have made in the past, and that we are currently exploring via tools like CRISPR: DNA is basically life’s file system. The analysis programs are reading a DNA strand’s bases (cytosine, thymine etc, the A, T, G, and C we all know) and turning them into binary data. Suppose those nucleotides were encoding binary data in the first place? After all, it’s been done before — right down the hall.
Here comes the mad science
Here’s how they did it. All you really need to know about the transcription application is that it reads the raw data coming from the transcription process and sorts through it, looking for patterns and converting the base sequences it finds into binary code.
“The conversion from ASCII As, Ts, Gs, and Cs into a stream of bits is done in a fixed-size buffer that assumes a reasonable maximum read length,” explained co-author Karl Koscher in response to my requests for more technical information.
That makes it ripe for a basic buffer overflow attack in which programs execute arbitrary code because it falls outside expected parameters. (They cheated a little by introducing a particular vulnerability into the software themselves, but they also point out that similar ones are present elsewhere, just not as conveniently for purposes of demonstration.)
After developing a way to include executable code in the base sequence, they set about making the exploit itself. Ironically, it’s inaccurate to call it a virus, although it’s closer to a “real” virus than perhaps any malicious code ever written.
“The exploit was 176 bases long,” Koscher wrote. “The compression program translates each base into two bits, which are packed together, resulting in a 44 byte exploit when translated.”
Given that there are 4 bases, it would make sense to have each represent a binary pair. Koscher confirmed this was the case. (If you’re curious, as I was: A=00, C=01, G=10, T=11.)
 “Most of these bytes are used to encode an ASCII shell command,” he continued. “Four bytes are used to make the conversion function return to the system() function in the C standard library, which executes shell commands, and four more bytes were used to tell system() where the command is in memory.”
“Most of these bytes are used to encode an ASCII shell command,” he continued. “Four bytes are used to make the conversion function return to the system() function in the C standard library, which executes shell commands, and four more bytes were used to tell system() where the command is in memory.”
Essentially the code in the DNA escapes the program as soon as it is converted from ACGTs to 00011011s, and executes some commands in the system — a sufficient demonstration of the existence of the threat vector. And there’s plenty of room for more code if you wanted to do more than break out of the app.
At 176 bases, the DNA strand comprising the exploit is “by almost any biological standard, very small,” said Lee Organick, a research scientist who worked on the project.
Biopunk future confirmed
In pursuance of every science journalist’s prime directive, which is to take interesting news and turn it into an existential threat to humanity, I had more questions for the team.
“CONCEIVABLY,” I asked, in all caps to emphasize that we were entering speculative territory, “could such a payload be delivered via, for example, a doctored blood sample or even directly from a person’s body? One can imagine a person whose DNA is essentially deadly to poorly secured computers.”
Irresponsibly, Organick stoked the fires of my fearmongering.
 “A doctored biological sample could indeed be used as a vector for malicious DNA to get processed downstream after sequencing and be executed,” she wrote.
“A doctored biological sample could indeed be used as a vector for malicious DNA to get processed downstream after sequencing and be executed,” she wrote.
“However, getting the malicious DNA strand from a doctored sample into the sequencer is very difficult with many technical challenges,” he continued. “Even if you were successfully able to get it into the sequencer for sequencing, it might not be in any usable shape (it might be too fragmented to be read usefully, for example).”
It’s not quite the biopunk apocalypse I envisioned, but the researchers do want people thinking along these lines at least as potential avenues of attack.
“We do want scientists thinking about this so they can hold the DNA analysis software they write to the appropriate security standards so that this never makes sense to become a potential attack vector in the first place,” said Organick.
“I would treat any input as untrusted and potentially able to compromise these applications,” added Koscher. “It would be wise to run these applications with some sort of isolation (in containers, VMs, etc.) to contain the damage an exploit could do. Many of these applications are also run as publicly-available cloud services, and I would make isolating these instances a high priority.”
The likelihood of an attack like this actually being pulled off is minuscule, but it’s a symbolic milestone in the increasing overlap between the digital and the biological.
The researchers will present their findings and process (PDF) next week at the USENIX Security conference in Vancouver.






























Comment